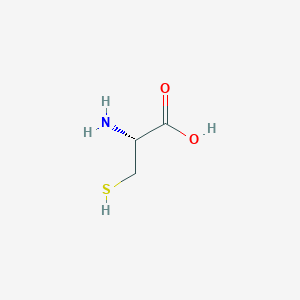
| Full List of Protein(s) Regulating This Metabolite |
| Amino acid/auxin permease (AAAP) |
|---|
| Solute carrier family 38 member 3 (SLC38A3) |
Click to Show/Hide the Full List of Regulating Pair(s): 2 Pair(s)
|
| Detailed Information |
Protein Info
 click to show the details of this protein click to show the details of this protein
|
| Regulating Pair (1) |
Experim Info
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
|
[2] |
| Introduced Variation |
Knockout of Slc38a3 |
| Induced Change |
Cysteine concentration: increase |
| Summary |
Introduced Variation

 Induced Change
Induced Change

|
| Disease Status |
Healthy individual
|
| Details |
It is reported that knockout of Slc38a3 leads to the increase of cysteine levels compared with control group. |
| Regulating Pair (2) |
Experim Info
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
|
[2] |
| Introduced Variation |
Knockout of SLC38A3 |
| Induced Change |
Cysteine concentration: increase |
| Summary |
Introduced Variation

 Induced Change
Induced Change

|
| Disease Status |
Healthy individual
|
| Details |
It is reported that knockout of SLC38A3 leads to the increase of cysteine levels compared with control group. |
| Dicarboxylate/amino acid:cation symporter (DAACS) |
|---|
| Excitatory amino acid transporter 3 (SLC1A1) |
Click to Show/Hide the Full List of Regulating Pair(s): 2 Pair(s)
|
| Detailed Information |
Protein Info
 click to show the details of this protein click to show the details of this protein
|
| Regulating Pair (1) |
Experim Info
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
|
[3] |
| Introduced Variation |
Mutation (p.I395del) of SLC1A1 |
| Induced Change |
Cysteine concentration: decrease |
| Summary |
Introduced Variation

 Induced Change
Induced Change

|
| Disease Status |
Nephropathic cystinosis [ICD-11: 5C60]
|
| Details |
It is reported that mutation (p.I395del) of SLC1A1 leads to the decrease of cysteine levels compared with control group. |
| Regulating Pair (2) |
Experim Info
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
|
[3] |
| Introduced Variation |
Mutation (p.R445W) of SLC1A1 |
| Induced Change |
Cysteine concentration: decrease |
| Summary |
Introduced Variation

 Induced Change
Induced Change

|
| Disease Status |
Nephropathic cystinosis [ICD-11: 5C60]
|
| Details |
It is reported that mutation (p.R445W) of SLC1A1 leads to the decrease of cysteine levels compared with control group. |
| Neutral amino acid transporter A (SLC1A4) |
Click to Show/Hide the Full List of Regulating Pair(s): 1 Pair(s)
|
| Detailed Information |
Protein Info
 click to show the details of this protein click to show the details of this protein
|
| Regulating Pair |
Experim Info
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
|
[4] |
| Introduced Variation |
Overexpression of SLC1A4 |
| Induced Change |
Cysteine concentration: increase |
| Summary |
Introduced Variation

 Induced Change
Induced Change

|
| Disease Status |
Healthy individual
|
| Details |
It is reported that overexpression of SLC1A4 leads to the increase of cysteine levels compared with control group. |
| GPCR rhodopsin (GPCR-1) |
|---|
| Adrenergic receptor beta-3 (ADRB3) |
Click to Show/Hide the Full List of Regulating Pair(s): 1 Pair(s)
|
| Detailed Information |
Protein Info
 click to show the details of this protein click to show the details of this protein
|
| Regulating Pair |
Experim Info
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
|
[5] |
| Introduced Variation |
Agonist (CL-316,243) of Adrb3 |
| Induced Change |
Cysteine concentration: increase |
| Summary |
Introduced Variation

 Induced Change
Induced Change

|
| Disease Status |
Healthy individual
|
| Details |
It is reported that agonist of ADRB3 leads to the increase of cysteine levels compared with control group. |
| GPCR secretin (GPCR-2) |
|---|
| Glucagon receptor (GCGR) |
Click to Show/Hide the Full List of Regulating Pair(s): 1 Pair(s)
|
| Detailed Information |
Protein Info
 click to show the details of this protein click to show the details of this protein
|
| Regulating Pair |
Experim Info
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
|
[6] |
| Introduced Variation |
Knockout of Gcgr |
| Induced Change |
Cysteine concentration: increase (FC = 2.7) |
| Summary |
Introduced Variation

 Induced Change
Induced Change

|
| Disease Status |
Type 2 diabetes mellitus [ICD-11: 5A11]
|
| Details |
It is reported that knockout of GCGR leads to the increase of cysteine levels compared with control group. |
| Hydrolases (EC 3) |
|---|
| Alpha-N-acetylglucosaminidase (NAGLU) |
Click to Show/Hide the Full List of Regulating Pair(s): 1 Pair(s)
|
| Detailed Information |
Protein Info
 click to show the details of this protein click to show the details of this protein
|
| Regulating Pair |
Experim Info
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
|
[7] |
| Introduced Variation |
Knockout of Naglu |
| Induced Change |
Cysteine concentration: decrease |
| Summary |
Introduced Variation

 Induced Change
Induced Change

|
| Disease Status |
Lysosomal storage diseases [ICD-11: 5C56]
|
| Details |
It is reported that knockout of Naglu leads to the decrease of cysteine levels compared with control group. |
| Sulfatase sulf-1 (SULF1) |
Click to Show/Hide the Full List of Regulating Pair(s): 1 Pair(s)
|
| Detailed Information |
Protein Info
 click to show the details of this protein click to show the details of this protein
|
| Regulating Pair |
Experim Info
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
|
[8] |
| Introduced Variation |
Knockdown (shRNA) of SULF1 |
| Induced Change |
Cysteine concentration: increase (FC = 8.91 - 10.32) |
| Summary |
Introduced Variation

 Induced Change
Induced Change

|
| Disease Status |
Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73]
|
| Details |
It is reported that knockdown of SULF1 leads to the increase of cysteine levels compared with control group. |
| Oxidoreductases (EC 1) |
|---|
| L-2-hydroxyglutarate dehydrogenase (L2HGDH) |
Click to Show/Hide the Full List of Regulating Pair(s): 1 Pair(s)
|
| Detailed Information |
Protein Info
 click to show the details of this protein click to show the details of this protein
|
| Regulating Pair |
Experim Info
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
|
[9] |
| Introduced Variation |
Mutation (Nonsense mutations or missense mutations) of L2hgdh |
| Induced Change |
Cysteine concentration: increase |
| Summary |
Introduced Variation

 Induced Change
Induced Change

|
| Disease Status |
Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30]
|
| Details |
It is reported that mutation (nonsense mutations or missense mutations leading to KMT2D loss) of L2hgdh leads to the increase of cysteine levels compared with control group. |
| Transcription factor (TF) |
|---|
| Myc proto-oncogene protein (MYC) |
Click to Show/Hide the Full List of Regulating Pair(s): 1 Pair(s)
|
| Detailed Information |
Protein Info
 click to show the details of this protein click to show the details of this protein
|
| Regulating Pair |
Experim Info
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
|
[10] |
| Introduced Variation |
Knockdown (siRNA) of MYC |
| Induced Change |
Cysteine concentration: decrease |
| Summary |
Introduced Variation

 Induced Change
Induced Change

|
| Disease Status |
Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91]
|
| Details |
It is reported that knockdown of MYC leads to the decrease of cysteine levels compared with control group. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair