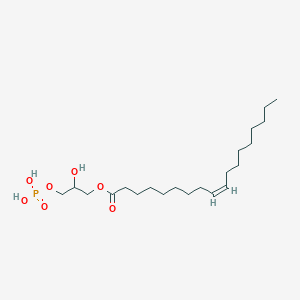
Details of Metabolite
| Full List of Protein(s) Regulated by This Metabolite | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPCR rhodopsin (GPCR-1) | ||||||
| Lysophosphatidate-3 receptor (LPAR3) | Click to Show/Hide the Full List of Regulating Pair(s): 1 Pair(s) | |||||
| Detailed Information |
Protein Info
 click to show the details of this protein click to show the details of this protein
|
|||||
| Regulating Pair |
Experim Info
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
|
[1] | ||||
| Introduced Variation | LysoPA(18:1(9Z)/0:0) addition (1 hours) | |||||
| Induced Change | LPAR3 protein expression levels: increase | |||||
| Summary | Introduced Variation
|
|||||
| Disease Status | Motor neuron disease [ICD-11: 8B60] | |||||
| Details | It is reported that lysoPA(18:1(9Z)/0:0) addition causes the increase of LPAR3 protein expression compared with control group. | |||||
| Transferases (EC 2) | ||||||
| Signal-regulated kinase 1 (ERK1) | Click to Show/Hide the Full List of Regulating Pair(s): 1 Pair(s) | |||||
| Detailed Information |
Protein Info
 click to show the details of this protein click to show the details of this protein
|
|||||
| Regulating Pair |
Experim Info
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
|
[2] | ||||
| Introduced Variation | LysoPA(18:1(9Z)/0:0) addition (0.08 hours) | |||||
| Induced Change | MAPK3 protein phosphorylation levels: increase | |||||
| Summary | Introduced Variation
|
|||||
| Disease Status | Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis [ICD-11: CB03] ... | |||||
| Details | It is reported that lysoPA(18:1(9Z)/0:0) addition causes the increase of MAPK3 protein phosphorylation compared with control group. | |||||
| Signal-regulated kinase 2 (ERK2) | Click to Show/Hide the Full List of Regulating Pair(s): 1 Pair(s) | |||||
| Detailed Information |
Protein Info
 click to show the details of this protein click to show the details of this protein
|
|||||
| Regulating Pair |
Experim Info
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
|
[2] | ||||
| Introduced Variation | LysoPA(18:1(9Z)/0:0) addition (0.08 hours) | |||||
| Induced Change | MAPK1 protein phosphorylation levels: increase | |||||
| Summary | Introduced Variation
|
|||||
| Disease Status | Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis [ICD-11: CB03] ... | |||||
| Details | It is reported that lysoPA(18:1(9Z)/0:0) addition causes the increase of MAPK1 protein phosphorylation compared with control group. | |||||
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Zhang and Dr. Mou.