| Synonyms |
Click to Show/Hide Synonyms of This Metabolite
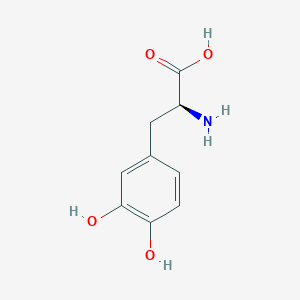
(-)-3-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-L-alanine; (-)-Dopa; (2S)-2-Amino-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)propanoate; (2S)-2-Amino-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)propanoic acid; 3 Hydroxy L tyrosine; 3,4-DIHYDROXYPHENYLALANINE; 3,4-Dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine; 3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl-L-alanine; 3-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-L-alanine; 3-Hydroxy-L-tyrosine; Bendopa; Cidandopa; Dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine; Dihydroxyphenylalanine; Dopaflex; Dopaidan; Dopal; Dopalina; Dopar; Doparkine; Doparl; Dopasol; Dopaston; Dopastone; Dopastral; Dopicar; Doprin; Eldopal; Eldopar; Eldopatec; Eurodopa; Helfo-dopa; Insulamina; L 3,4 Dihydroxyphenylalanine; L Dopa; L-(-)-Dopa; L-3,4-Dihydroxyphenylalanine; L-3-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-alanine; L-4-5-Dihydroxyphenylalanine; L-Dihydroxyphenylalanine; L-b-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-a-alanine; L-beta-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-alpha-alanine; L-beta-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)alanine; Laradopa; Larodopa; Ledopa; Levedopa; Levodopa; Levodopum; Levopa; Maipedopa; Medphano brand OF levodopa; Parda; Pardopa; Prodopa; Roberts brand OF levodopa; Roche brand OF levodopa; Syndopa; Veldopa; Weldopa; b-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-a-L-alanine; beta-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-L-alanine; beta-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-alpha-L-alanine; beta-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)alanine
|
| Structure Type |
Amino acids, peptides, and analogues (Click to Show/Hide the Complete Structure Type Hierarchy)
Organic acids and derivatives
Carboxylic acids and derivatives
Amino acids, peptides, and analogues
|
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair