|
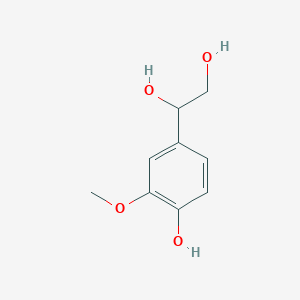
Vanylglycol, also known as MHPG or MOPEG, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as methoxyphenols. Methoxyphenols are compounds containing a methoxy group attached to the benzene ring of a phenol moiety. Vanylglycol is an extremely weak basic (essentially neutral) compound (based on its pKa). Catecholamines play an important role in platelet activation and aggregation, epinephrine being the most potent one. vanylglycol and pyrocatechol can be biosynthesized from 3,4-dihydroxyphenylglycol and guaiacol; which is catalyzed by the enzyme catechol O-methyltransferase. Vanylglycol (MHPG) is a O-methylated metabolite of normetanephrine. In humans, vanylglycol is involved in the metabolic disorder called tyrosinemia, transient, of the newborn. Alcohol consumption increases the level of Vanylglycol in urine and CSF. Vanylglycol is found normally in urine, in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid. Outside of the human body, vanylglycol has been detected, but not quantified in, several different foods, such as blackcurrants, chinese bayberries, elderberries, oriental wheats, and poppies. This could make vanylglycol a potential biomarker for the consumption of these foods. Catecholamines are substantially increased during stress, exercise or smoking and could result in clinically important platelet activation if their action was not rapidly regulated. Vanylglycol has been found to be associated with several diseases such as multi-infarct dementia, epilepsy, hereditary spastic paraplegia, and schizophrenia; also vanylglycol has been linked to the inborn metabolic disorders including aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency. Vanylglycol is formed by catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) from norepinephrine. Alcohol dehydrogenase has been shown to act on norepinephrine and produce HMPG.
|
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair