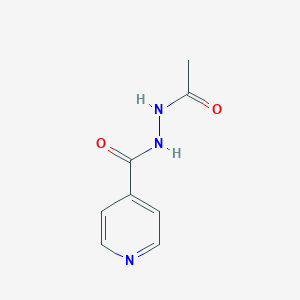
| Full List of Protein(s) Regulating This Metabolite |
| Transferases (EC 2) |
|---|
| Arylamine N-acetyltransferase 1 (NAT1) |
Click to Show/Hide the Full List of Regulating Pair(s): 2 Pair(s)
|
| Detailed Information |
Protein Info
 click to show the details of this protein click to show the details of this protein
|
| Regulating Pair (1) |
Experim Info
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
|
[1] |
| Introduced Variation |
Knockout of Nat1 |
| Induced Change |
Acetylhydrazine concentration: decrease |
| Summary |
Introduced Variation

 Induced Change
Induced Change

|
| Disease Status |
Healthy individual
|
| Details |
It is reported that knockout of NAT leads to the decrease of acetylhydrazine levels compared with control group. |
| Regulating Pair (2) |
Experim Info
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
|
[1] |
| Introduced Variation |
Knockout of Nat1 |
| Induced Change |
Acetylhydrazine concentration: decrease |
| Summary |
Introduced Variation

 Induced Change
Induced Change

|
| Disease Status |
Healthy individual
|
| Details |
It is reported that knockout of NAT leads to the decrease of acetylhydrazine levels compared with control group. |
| Arylamine N-acetyltransferase 2 (NAT2) |
Click to Show/Hide the Full List of Regulating Pair(s): 2 Pair(s)
|
| Detailed Information |
Protein Info
 click to show the details of this protein click to show the details of this protein
|
| Regulating Pair (1) |
Experim Info
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
|
[1] |
| Introduced Variation |
Knockout of Nat2 |
| Induced Change |
Acetylhydrazine concentration: decrease |
| Summary |
Introduced Variation

 Induced Change
Induced Change

|
| Disease Status |
Healthy individual
|
| Details |
It is reported that knockout of NAT leads to the decrease of acetylhydrazine levels compared with control group. |
| Regulating Pair (2) |
Experim Info
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
|
[1] |
| Introduced Variation |
Knockout of Nat2 |
| Induced Change |
Acetylhydrazine concentration: decrease |
| Summary |
Introduced Variation

 Induced Change
Induced Change

|
| Disease Status |
Healthy individual
|
| Details |
It is reported that knockout of NAT leads to the decrease of acetylhydrazine levels compared with control group. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair