| General Information of MET (ID: META01214) |
| Name |
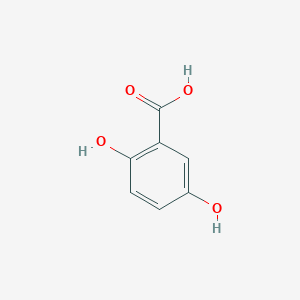
2,5-Dihydroxybenzoic acid
|
| Synonyms |
Click to Show/Hide Synonyms of This Metabolite
2,5-DIHYDROXYBENZOIC ACID; gentisic acid; 490-79-9; Benzoic acid, 2,5-dihydroxy-; Hydroquinonecarboxylic acid; Gentisate; 5-Hydroxysalicylic acid; Gensigen; Gensigon; 2,5-Dioxybenzoic acid; 2,5-Dhba; Gentisinic acid; Salicylic acid, 5-hydroxy-; Kyselina gentisinova; Gentisinate; UNII-VP36V95O3T; MFCD00002460; NSC 27224; Kyselina 2,5-dihydroxybenzoova; 3,6-dihydroxybenzoic acid; 2,5-Dihydroxy benzoic acid; CHEMBL1461; VP36V95O3T; CHEBI:17189; BENZOIC ACID,2,5-DIHYDROXY; Gentinatre; Gentalpin; Gentasol
|
| Source |
Aromatic homomonocyclic compounds
|
| Structure Type |
Benzoic acids and derivatives (Click to Show/Hide the Complete Structure Type Hierarchy)
Benzenoids
Benzene and substituted derivatives
Benzoic acids and derivatives
|
| PubChem CID |
|
| HMDB ID |
|
| Formula |
C7H6O4
|
| Structure |
<iframe style="width: 300px; height: 300px;" frameborder="0" src="https://embed.molview.org/v1/?mode=balls&cid=3469"></iframe>
|
 |
|
3D MOL
|
2D MOL
|
|
Click to Show/Hide the Molecular/Functional Data (External Links/Property/Function) of This Metabolite
|
| KEGG ID |
|
| ChEBI ID |
|
| FooDB ID |
|
| ChemSpider ID |
|
| METLIN ID |
|
| Physicochemical Properties |
Molecular Weight |
154.12 |
Topological Polar Surface Area |
77.8 |
| XlogP |
1.6 |
Complexity |
157 |
| Heavy Atom Count |
11 |
Rotatable Bond Count |
1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
3 |
Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
4 |
| Function |
Gentisic acid, also known as gentisate or 2,5-dioxybenzoate, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as hydroxybenzoic acid derivatives. Hydroxybenzoic acid derivatives are compounds containing a hydroxybenzoic acid (or a derivative), which is a benzene ring bearing a carboxyl and a hydroxyl groups. Gentisic acid is an extremely weak basic (essentially neutral) compound (based on its pKa). Gentisic acid exists in all living organisms, ranging from bacteria to humans. Outside of the human body, Gentisic acid is found, on average, in the highest concentration within a few different foods, such as tarragons, common thymes, and common sages and in a lower concentration in grape wines, rosemaries, and sweet marjorams. Gentisic acid has also been detected, but not quantified in, several different foods, such as common grapes, fennels, german camomiles, evening primroses, and guava. This could make gentisic acid a potential biomarker for the consumption of these foods. Gentisic acid is also a byproduct of tyrosine and benzoate metabolism. There is an increasing amount of evidence indicating that gentisic acid has a broad spectrum of biological activity, such as anti-inflammatory, antirheumatic and antioxidant properties. Gentisic acid is an active metabolite of salicylic acid degradation. It is a crystalline powder that forms monoclinic prism in water solution. It is a fungal metabolite as well (ChEBI). Gentisic acid is a dihydroxybenzoic acid.
|
|
Regulatory Network
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair

