| General Information of MET (ID: META00847) |
| Name |
Acetyl-N-formyl-5-methoxykynurenamine
|
| Synonyms |
Click to Show/Hide Synonyms of This Metabolite
AFMK; Formyl-N-acetyl-5-methoxykynurenamine; K1; N-Acetyl-N-formyl-5-methoxykynurenamine; N-[3-(2-Formamido-5-methoxy-phenyl)-3-oxo-propyl]acetamide; N1-Acetyl-N2-formyl-5-methoxykynurenine; NSC 688263
|
| Source |
Endogenous;Food
|
| Structure Type |
Carbonyl compounds (Click to Show/Hide the Complete Structure Type Hierarchy)
Organic oxygen compounds
Organooxygen compounds
Carbonyl compounds
|
| PubChem CID |
|
| HMDB ID |
|
| Formula |
C13H16N2O4
|
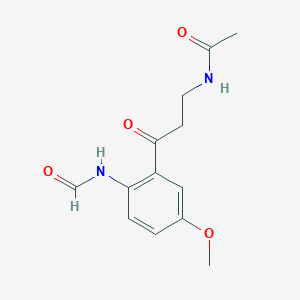
| Structure |
<iframe style="width: 300px; height: 300px;" frameborder="0" src="https://embed.molview.org/v1/?mode=balls&cid=171161"></iframe>
|
 |
|
3D MOL
|
2D MOL
|
|
Click to Show/Hide the Molecular/Functional Data (External Links/Property/Function) of This Metabolite
|
| KEGG ID |
|
| FooDB ID |
|
| ChemSpider ID |
|
| Physicochemical Properties |
Molecular Weight |
264.28 |
Topological Polar Surface Area |
84.5 |
| XlogP |
0.6 |
Complexity |
333 |
| Heavy Atom Count |
19 |
Rotatable Bond Count |
6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
2 |
Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
4 |
| Function |
Acetyl-N-formyl-5-methoxykynurenamine (AFMK) results from the oxidative cleavage of the pyrrole ring during melatonin oxidation by myeloperoxidase (MPO), a superoxide anion (O)-dependent reaction. AFMK is also expected to be formed from oxidation catalyzed by the unspecific enzyme indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), found in a variety of cell types including monocyte/macrophage lineages. MPO- and IDO-catalyzed melatonin oxidation has the requirement of O in common, a species formed in large amounts in inflammatory conditions. The non-enzymatic formation of AFMK can also be expected by its direct reaction with highly reactive oxygen species, such as hydroxyl radical and singlet oxygen. Thus, we assume that AFMK is a product formed in a route of melatonin metabolism, especially active in inflammation. As AFMK is biologically more active on leukocytes than melatonin, the metabolizing of melatonin to AFMK at inflammatory sites possibly plays a role in immunomodulation. AFMK is found in the CSF of patients with meningitis, and in some samples at a remarkably high concentration. AFMK was also found in some patients to exceed the concentration of melatonin normally found in serum.
|
|
Regulatory Network
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair

