| General Information of MET (ID: META00783) |
| Name |
Aspartylglycosamine
|
| Synonyms |
Click to Show/Hide Synonyms of This Metabolite
(N-g-(2-Acetamido-2-deoxy-b-D-gluco-pyranosyl)-L-asparagine; (N-gamma-(2-Acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-gluco-pyranosyl)-L-asparagine; (N-gamma-(2-Acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-delta-gluco-pyranosyl)-L-asparagine; 1-beta-Aspartyl-N-acetyl-D-glucosaminylamine; 2-Acetamido-1-(beta-L-aspartamido)-1,2-dideoxy-beta-D-glucose', 2-Acetamido-1-N-(4'-L-aspartyl)-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranosylamine, '2-Acetamido-N-L-beta-aspartyl-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranosylamine; 2-Acetamido-1-b-(L-aspartamido)-1,2-dideoxy-D-glucose; 2-Acetamido-1-beta-(L-aspartamido)-1,2-dideoxy-D-glucose; 2-Acetamido-1-beta-(L-aspartamido)-1,2-dideoxy-delta-glucose', 2-Acetamido-1-N-(4'-L-aspartyl)-2-deoxy-beta-delta-glucopyranosylamine, '4-N-2-Acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-L-asparagine; 2-Acetamido-N(1)-L-beta-aspartyl-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranosylamine; 4-N-2-Acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-delta-glucopyranosyl-L-asparagine; AADG; Acetylglucosaminylasparagine; Asparaginylglucosamine; Aspartylglucosamine; Aspartylglucosylamine; Aspartylglycosamine; H-Asn(glcnac-b-D)-OH; H-Asn(glcnac-beta-D)-OH; N(4)-(2-Acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranosyl)-L-asparagine; N(4)-(2-Acetamido-2-deoxyglucopyranosyl)asparagine; N(4)-(Acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminyl)asparagine; N(4)-(beta-N-Acetyl-D-glucosaminyl)-L-asparagine; N-(2-(Acetylamino)-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranosyl)L-asparagine; N-(2-(Acetylamino)-2-deoxy-beta-delta-glucopyranosyl)L-asparagine; N-(2-Acetylamino)-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-L-asparagine; N-(2-Acetylamino)-2-deoxy-beta-delta-glucopyranosyl-L-asparagine; N-ADGP-asn; N-Acetylglucosaminylasparagine; N4-(Acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminyl)asparagine; N4-(beta-N-Acetyl-D-glucosaminyl)-L-asparagine; b-D-GlcNAc-1->n-asn; beta-D-GlcNAc-1->n-asn; beta-N-Acetylglucosaminyl-L-asparagine; beta-delta-GlcNAc-1->n-asn
|
| Source |
Endogenous;Food
|
| Structure Type |
Carbohydrates and carbohydrate conjugates (Click to Show/Hide the Complete Structure Type Hierarchy)
Organic oxygen compounds
Organooxygen compounds
Carbohydrates and carbohydrate conjugates
|
| PubChem CID |
|
| HMDB ID |
|
| Formula |
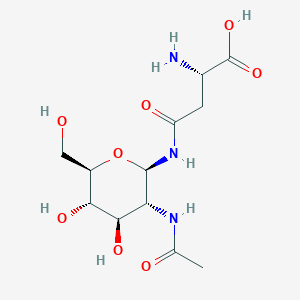
C12H21N3O8
|
| Structure |
<iframe style="width: 300px; height: 300px;" frameborder="0" src="https://embed.molview.org/v1/?mode=balls&cid=123826"></iframe>
|
 |
|
3D MOL
|
2D MOL
|
|
Click to Show/Hide the Molecular/Functional Data (External Links/Property/Function) of This Metabolite
|
| KEGG ID |
|
| ChEBI ID |
|
| FooDB ID |
|
| ChemSpider ID |
|
| METLIN ID |
|
| Physicochemical Properties |
Molecular Weight |
335.31 |
Topological Polar Surface Area |
191 |
| XlogP |
-5.7 |
Complexity |
460 |
| Heavy Atom Count |
23 |
Rotatable Bond Count |
6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
7 |
Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
9 |
| Function |
Aspartylglycosamine, also known as n4-(beta-N-acetyl-D-glucosaminyl)-L-asparagine or 1-beta-aspartyl-N-acetyl-D-glucosaminylamine, is a member of the class of compounds known as glycosylamines. Glycosylamines are compounds consisting of an amine with a beta-N-glycosidic bond to a carbohydrate, thus forming a cyclic hemiaminal ether bond (alpha-amino ether). Aspartylglycosamine is soluble (in water) and a moderately acidic compound (based on its pKa). Aspartylglycosamine can be found primarily in urine, as well as in human spleen tissue. Within the cell, aspartylglycosamine is primarily located in the cytoplasm. Moreover, aspartylglycosamine is found to be associated with aspartylglucosaminuria, which is an inborn error of metabolism. Large amount of aspartylglycosamine appears in patients with aspartylglycosaminuria corresponding to decreased activity of aspartylglycosamine amido hydrolase.
|
|
Regulatory Network
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair

