| General Information of MET (ID: META00760) |
| Name |
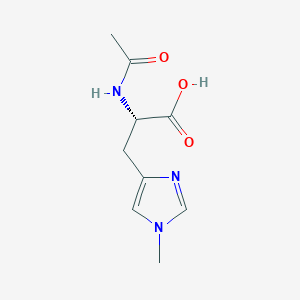
N-Acetyl-1-methylhistidine
|
| Synonyms |
Click to Show/Hide Synonyms of This Metabolite
N-Acetyl-1-methylhistidine
|
| Source |
Aromatic heteromonocyclic compounds
|
| Structure Type |
Amino acids, peptides, and analogues (Click to Show/Hide the Complete Structure Type Hierarchy)
Organic acids and derivatives
Carboxylic acids and derivatives
Amino acids, peptides, and analogues
|
| PubChem CID |
|
| HMDB ID |
|
| Formula |
C9H13N3O3
|
| Structure |
<iframe style="width: 300px; height: 300px;" frameborder="0" src="https://embed.molview.org/v1/?mode=balls&cid=53859791"></iframe>
|
 |
|
3D MOL
|
2D MOL
|
|
Click to Show/Hide the Molecular/Functional Data (External Links/Property/Function) of This Metabolite
|
| ChEBI ID |
|
| ChemSpider ID |
|
| Physicochemical Properties |
Molecular Weight |
211.22 |
Topological Polar Surface Area |
84.2 |
| XlogP |
-0.7 |
Complexity |
257 |
| Heavy Atom Count |
15 |
Rotatable Bond Count |
4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
2 |
Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
4 |
| Function |
N-Acetyl-1-methylhistidine belongs to the class of organic compounds known as histidine and derivatives. Histidine and derivatives are compounds containing histidine or a derivative thereof resulting from a reaction of histidine at the amino group or the carboxy group, or from the replacement of any hydrogen of glycine by a heteroatom. N-Acetyl-1-methylhistidine is an acetylated derivative of 1-methylhistidine and a very strong basic compound (based on its pKa). It has been found to be associated with chronic kidney disease: the higher the N-acetyl-1-methylhistidine levels, the lower the estimated glomerular filtration rate. This could make N-acetyl-1-methylhistidine a biomarker for chronic kidney disease.
|
|
Regulatory Network
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair

