| General Information of MET (ID: META00629) |
| Name |
20-COOH-leukotriene E4
|
| Synonyms |
Click to Show/Hide Synonyms of This Metabolite
20-COOH-LTE4; 6-(S-Cysteinyl)-(5S)-hydroxy-(7E,9E,11Z,14Z)-eicosatetraenedioate; 6-(S-Cysteinyl)-(5S)-hydroxy-(7E,9E,11Z,14Z)-eicosatetraenedioic acid
|
| Source |
Endogenous;Fatty acyls;Food
|
| Structure Type |
Amino acids, peptides, and analogues (Click to Show/Hide the Complete Structure Type Hierarchy)
Organic acids and derivatives
Carboxylic acids and derivatives
Amino acids, peptides, and analogues
|
| PubChem CID |
|
| HMDB ID |
|
| Formula |
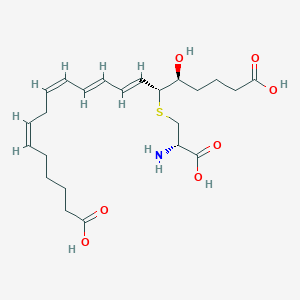
C23H35NO7S
|
| Structure |
<iframe style="width: 300px; height: 300px;" frameborder="0" src="https://embed.molview.org/v1/?mode=balls&cid=53481508"></iframe>
|
 |
|
3D MOL is unavailable
|
2D MOL
|
|
Click to Show/Hide the Molecular/Functional Data (External Links/Property/Function) of This Metabolite
|
| FooDB ID |
|
| Physicochemical Properties |
Molecular Weight |
469.6 |
Topological Polar Surface Area |
183 |
| XlogP |
0.3 |
Complexity |
673 |
| Heavy Atom Count |
32 |
Rotatable Bond Count |
19 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
5 |
Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
9 |
| Function |
20-COOH-leukotriene E4 is a metabolite through lipid oxidation of Leukotriene E4 (LTE4).Leukotriene E4 (LTE4) is a cysteinyl leukotriene. Cysteinyl leukotrienes (CysLTs) are a family of potent inflammatory mediators that appear to contribute to the pathophysiologic features of allergic rhinitis. Nasal blockage induced by CysLTs is mainly due to dilatation of nasal blood vessels, which can be induced by the nitric oxide produced through CysLT1 receptor activation. LTE4, activate contractile and inflammatory processes via specific interaction with putative seven transmembrane-spanning receptors that couple to G proteins and subsequent intracellular signaling pathways. LTE4 is metabolized from leukotriene C4 in a reaction catalyzed by gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase and a particulate dipeptidase from kidney. Leukotrienes are eicosanoids. The eicosanoids consist of the prostaglandins (PGs), thromboxanes (TXs), leukotrienes (LTs), and lipoxins (LXs). The PGs and TXs are collectively identified as prostanoids. Prostaglandins were originally shown to be synthesized in the prostate gland, thromboxanes from platelets (thrombocytes), and leukotrienes from leukocytes, hence the derivation of their names. All mammalian cells except erythrocytes synthesize eicosanoids. These molecules are extremely potent, able to cause profound physiological effects at very dilute concentrations. All eicosanoids function locally at the site of synthesis, through receptor-mediated G-protein linked signalling pathways.
|
|
Regulatory Network
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair

