| General Information of MET (ID: META00525) |
| Name |
4-Acetamidobutanoic acid
|
| Synonyms |
Click to Show/Hide Synonyms of This Metabolite
4-(Acetylamino)butanoate; 4-(Acetylamino)butanoic acid; 4-Acetamidobutanoate; 4-Acetamidobutanoic acid; 4-Acetamidobutyrate; 4-Acetamidobutyric acid; N-Acetyl-4-aminobutanoate; N-Acetyl-4-aminobutanoic acid; N-Acetyl-4-aminobutyrate; N-Acetyl-4-aminobutyric acid; N-Acetyl-gaba; N-Acetyl-gamma-amino-N-butyric acid; N-Acetyl-gamma-aminobutyrate; N4-Acetylaminobutanoate; N4-Acetylaminobutanoic acid
|
| Source |
Endogenous;Yeast Metabolite;Food
|
| Structure Type |
Amino acids, peptides, and analogues (Click to Show/Hide the Complete Structure Type Hierarchy)
Organic acids and derivatives
Carboxylic acids and derivatives
Amino acids, peptides, and analogues
|
| PubChem CID |
|
| HMDB ID |
|
| Formula |
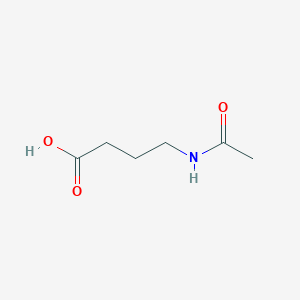
C6H11NO3
|
| Structure |
<iframe style="width: 300px; height: 300px;" frameborder="0" src="https://embed.molview.org/v1/?mode=balls&cid=18189"></iframe>
|
 |
|
3D MOL
|
2D MOL
|
|
Click to Show/Hide the Molecular/Functional Data (External Links/Property/Function) of This Metabolite
|
| KEGG ID |
|
| ChEBI ID |
|
| FooDB ID |
|
| ChemSpider ID |
|
| Physicochemical Properties |
Molecular Weight |
145.16 |
Topological Polar Surface Area |
66.4 |
| XlogP |
-0.6 |
Complexity |
133 |
| Heavy Atom Count |
10 |
Rotatable Bond Count |
4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
2 |
Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
3 |
| Function |
4-Acetamidobutanoic acid, also known as 4-acetamidobutanoate or N-acetyl-4-aminobutyric acid, is a member of the class of compounds known as gamma amino acids and derivatives. These compounds are amino acids having an -NH2 group attached to the gamma carbon atom. 4-Acetamidobutanoic acid is soluble (in water) and a weakly acidic compound (based on its pKa). 4-Acetamidobutanoic acid can be found in a number of food items such as Rubus species (blackberry, raspberry), cassava, pepper (C. frutescens), and napa cabbage, which makes 4-acetamidobutanoic acid a potential biomarker for the consumption of these food products. 4-Acetamidobutanoic acid can be found in blood, feces, and urine, as well as in human prostate tissue. 4-Acetamidobutanoic acid exists in all eukaryotes, ranging from yeast to humans. 4-Acetamidobutanoic acid is a GABA derivative, a product of the urea cycle and the metabolism of amino groups, and the product of NAD-linked aldehyde dehydrogenase (EC 1.2.1.3) (KEGG).
|
|
Regulatory Network
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair

