| General Information of MET (ID: META00497) |
| Name |
O-Acetylserine
|
| Synonyms |
Click to Show/Hide Synonyms of This Metabolite
L-Serine, acetate (ester); L-Serine, acetic acid (ester); O-Acetyl-L-serine; O-Acetyl-serine; O-Acetylserine; O-Acetylserine hydrobromide, (D)-isomer; O-Acetylserine, (L)-isomer; O3-Acetyl-L-serine; Serine acetate ester
|
| Source |
Endogenous;Escherichia Coli Metabolite;Yeast Metabolite;Food;Drug
|
| Structure Type |
Amino acids, peptides, and analogues (Click to Show/Hide the Complete Structure Type Hierarchy)
Organic acids and derivatives
Carboxylic acids and derivatives
Amino acids, peptides, and analogues
|
| PubChem CID |
|
| HMDB ID |
|
| Formula |
C5H9NO4
|
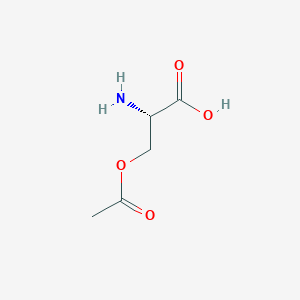
| Structure |
<iframe style="width: 300px; height: 300px;" frameborder="0" src="https://embed.molview.org/v1/?mode=balls&cid=99478"></iframe>
|
 |
|
3D MOL
|
2D MOL
|
|
Click to Show/Hide the Molecular/Functional Data (External Links/Property/Function) of This Metabolite
|
| KEGG ID |
|
| DrugBank ID |
|
| ChEBI ID |
|
| FooDB ID |
|
| ChemSpider ID |
|
| METLIN ID |
|
| Physicochemical Properties |
Molecular Weight |
147.13 |
Topological Polar Surface Area |
89.6 |
| XlogP |
-3.5 |
Complexity |
145 |
| Heavy Atom Count |
10 |
Rotatable Bond Count |
4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
2 |
Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
5 |
| Function |
O-Acetylserine (OASS) is an acylated amino acid derivative. It is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of the common amino acid cysteine in bacteria and plants. Its presence in humans arises from either microbial metabolism in the gut or through consumption of foods containing OASS.
|
|
Regulatory Network
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair

