| General Information of MET (ID: META00475) |
| Name |
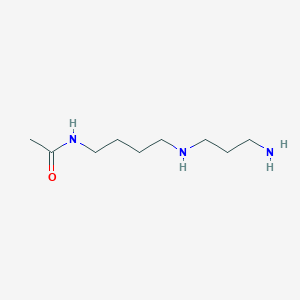
N8-Acetylspermidine
|
| Synonyms |
Click to Show/Hide Synonyms of This Metabolite
N(8)-Acetylspermidine; N(8)-Acetylspermidine dihydrochloride; N(8)-Monoacetylspermidine; N-[4-[(3-Aminopropyl)amino]butyl]-acetamide; N-[4-[(3-Aminopropyl)amino]butyl]acetamide; N8-Acetylspermidine; N8-Monoacetylspermidine
|
| Source |
Endogenous;Escherichia Coli Metabolite;Yeast Metabolite;Food
|
| Structure Type |
Carboximidic acids (Click to Show/Hide the Complete Structure Type Hierarchy)
Organic acids and derivatives
Carboximidic acids and derivatives
Carboximidic acids
|
| PubChem CID |
|
| HMDB ID |
|
| Formula |
C9H21N3O
|
| Structure |
<iframe style="width: 300px; height: 300px;" frameborder="0" src="https://embed.molview.org/v1/?mode=balls&cid=123689"></iframe>
|
 |
|
3D MOL
|
2D MOL
|
|
Click to Show/Hide the Molecular/Functional Data (External Links/Property/Function) of This Metabolite
|
| KEGG ID |
|
| ChEBI ID |
|
| FooDB ID |
|
| ChemSpider ID |
|
| METLIN ID |
|
| Physicochemical Properties |
Molecular Weight |
187.28 |
Topological Polar Surface Area |
67.2 |
| XlogP |
-0.8 |
Complexity |
128 |
| Heavy Atom Count |
13 |
Rotatable Bond Count |
8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
3 |
Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
3 |
| Function |
N8-Acetylspermidine is a polyamine. The polyamines, found in virtually all living organisms, are a ubiquitous group of compounds that appear to play a vital role in many cellular processes involving nucleic acids including cell growth and differentiation. Acetylation on the terminal nitrogen adjacent to the 4-carbon chain produces N8-acetylspermidine. This reaction is catalyzed by spermidine N8-acetyltransferase and does not result in the conversion of spermidine to putrescine. Instead, the product undergoes deacetylation. This acetyltransferase appears to be associated with chromatin in the cell nucleus and has been reported to be the same as (or related to) the enzyme(s) responsible for histone acetylation. N8-Acetylspermidine does not accumulate in tissues but rather appears to be rapidly deacetylated back to spermidine by a relatively specific cytosolic deacetylase, N8-acetylspermidine deacetylase. The function of this N8-acetylation/deacetylation pathway in cellular processes is not understood clearly, but several observations have suggested a role in cell growth and differentiation.
|
|
Regulatory Network
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair

