| General Information of MET (ID: META00462) |
| Name |
7-Methylxanthine
|
| Synonyms |
Click to Show/Hide Synonyms of This Metabolite
2,6-Dihydroxy-7-methylpurine; 3,7-Dihydro-7-methyl-1H-purine-2,6-dione; 7-Methyl-3,7-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione; 7-Methyl-7H-purine-2,6-diol; 7-Methylxanthin; 7-Methylxanthine, 7-(13)C-labeled; Heteroxanthin; Heteroxanthine; Methylxanthine
|
| Source |
Endogenous;Drug Metabolite;Food;Caffeine;Herbal Ingredients In-Vivo Metabolism
|
| Structure Type |
Purines and purine derivatives (Click to Show/Hide the Complete Structure Type Hierarchy)
Organoheterocyclic compounds
Imidazopyrimidines
Purines and purine derivatives
|
| PubChem CID |
|
| HMDB ID |
|
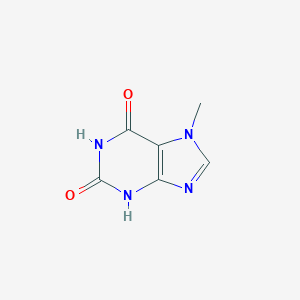
| Formula |
C6H6N4O2
|
| Structure |
<iframe style="width: 300px; height: 300px;" frameborder="0" src="https://embed.molview.org/v1/?mode=balls&cid=68374"></iframe>
|
 |
|
3D MOL
|
2D MOL
|
|
Click to Show/Hide the Molecular/Functional Data (External Links/Property/Function) of This Metabolite
|
| KEGG ID |
|
| ChEBI ID |
|
| FooDB ID |
|
| ChemSpider ID |
|
| Physicochemical Properties |
Molecular Weight |
166.14 |
Topological Polar Surface Area |
76 |
| XlogP |
-0.9 |
Complexity |
242 |
| Heavy Atom Count |
12 |
Rotatable Bond Count |
N.A. |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
2 |
Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
3 |
| Function |
7-Methylxanthine is a methyl derivative of xanthine, found occasionally in human urine. 7-Methylxanthine is one of the purine components in urinary calculi. Methylated purines originate from the metabolism of methylxanthines (caffeine, theophylline and theobromine). Caffeine is metabolized via successive pathways mainly catalyzed by CYP1A2, xanthine oxidase or N-acetyltransferase-2 to give 14 different metabolites, including 7-methylxanthine. CYP1A2 activity shows an inter-individual variability among the population. CYP1A2, an isoform of the CYP1A cytochrome P450 super-family, is involved in the metabolism of many drugs and plays a potentially important role in the induction of chemical carcinogenesis. Purine derivatives in urinary calculi could be considered markers of abnormal purine metabolism. The content of a purine derivative in stone depends on its average urinary excretion in the general population, similarity to the chemical structure of uric acid, and content of the latter in stone. This suggests that purines in stones represent a solid solution with uric acid as solvent. It is also plausible that methylxanthines, ubiquitous components of the diet and drugs, are involved in the pathogenesis of urolithiasis.
|
|
Regulatory Network
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair

