|
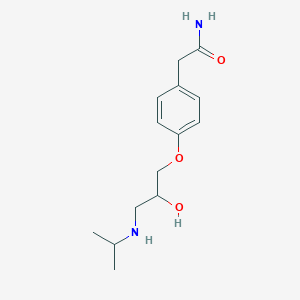
Atenolol is a so-called beta1-selective (or 'cardioselective') drug. That means that it exerts greater blocking activity on myocardial beta1-receptors than on beta2 ones in the lung. The beta2 receptors are responsible to keep the bronchial system open. If these receptors are blocked, bronchospasm with serious lack of oxygen in the body can result. However, due to its cardioselective properties, the risk of bronchospastic reactions if using atenolol is reduced compared to nonselective drugs as propranolol. Nonetheless, this reaction may also be encountered with atenolol, particularly with high doses. Extreme caution should be exerted if atenolol is given to asthma patients, who are particularly at risk; the dose should be as low as possible. If an asthma attack occurs, the inhalation of a beta2-mimetic antiasthmatic, such as hexoprenalin or salbutamol, will usually suppress the symptoms. Atenolol (trade name Tenormin) can be used to treat cardiovascular diseases such as hypertension, coronary heart disease, arrhythmias, and treatment of myocardial infarction after the acute event. Patients with compensated congestive heart failure may be treated with atenolol as a co medication (usually together with an ACE inhibitor, a diuretic and a digitalis-glycoside, if indicated). In patients with congestive heart failure, it reduces the need for and the consumption of oxygen of the heart muscle. It is very important to start with low doses, as atenolol reduces also the muscular power of the heart, which is an undesired effect in congestive heart failure.
|
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair