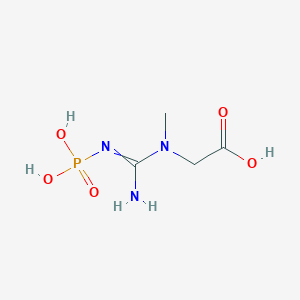
Details of Metabolite
| Full List of Protein(s) Regulating This Metabolite | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrolases (EC 3) | ||||||
| Leukotriene-C4 hydrolase (GGT1) | Click to Show/Hide the Full List of Regulating Pair(s): 1 Pair(s) | |||||
| Detailed Information |
Protein Info
 click to show the details of this protein click to show the details of this protein
|
|||||
| Regulating Pair |
Experim Info
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
|
[1] | ||||
| Introduced Variation | Knockdown (siRNA) of GGT1 | |||||
| Induced Change | Phosphocreatine concentration: increase | |||||
| Summary | Introduced Variation
|
|||||
| Disease Status | Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90] | |||||
| Details | It is reported that knockdown of GGT1 leads to the increase of phosphocreatine levels compared with control group. | |||||
| Pore-forming PNC peptide (PNC) | ||||||
| Cellular tumor antigen p53 (TP53) | Click to Show/Hide the Full List of Regulating Pair(s): 1 Pair(s) | |||||
| Detailed Information |
Protein Info
 click to show the details of this protein click to show the details of this protein
|
|||||
| Regulating Pair |
Experim Info
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
|
[2] | ||||
| Introduced Variation | Knockout of TP53 | |||||
| Induced Change | Phosphocreatine concentration: decrease (Log2 FC=0.93) | |||||
| Summary | Introduced Variation
|
|||||
| Disease Status | Colon cancer [ICD-11: 2B90] | |||||
| Details | It is reported that knockout of TP53 leads to the decrease of phosphocreatine levels compared with control group. | |||||
| Transcription factor (TF) | ||||||
| Forkhead box protein O1 (FOXO1) | Click to Show/Hide the Full List of Regulating Pair(s): 1 Pair(s) | |||||
| Detailed Information |
Protein Info
 click to show the details of this protein click to show the details of this protein
|
|||||
| Regulating Pair |
Experim Info
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
|
[3] | ||||
| Introduced Variation | Overexpression of Foxo1 | |||||
| Induced Change | Phosphocreatine concentration: decrease (FC = 0.80) | |||||
| Summary | Introduced Variation
|
|||||
| Disease Status | Healthy individual | |||||
| Details | It is reported that overexpression of Foxo1 leads to the decrease of phosphocreatine levels compared with control group. | |||||
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Zhang and Dr. Mou.