| Synonyms |
Click to Show/Hide Synonyms of This Metabolite
(3ALPHA,5ALPHA,12ALPHA)-3,12-DIHYDROXYCHOLAN-24-OIC ACID; (3a,5a,12a)-3,12-DIHYDROXYCHOLAN-24-Oate; (3a,5a,12a)-3,12-DIHYDROXYCHOLAN-24-Oic acid; (3a,5b,12a)-3,12-Dihydroxycholan-24-Oate; (3a,5b,12a)-3,12-Dihydroxycholan-24-Oic acid; (3alpha,5beta,12alpha)-3,12-Dihydroxycholan-24-Oic acid; 12beta-Isomer deoxycholic acid; 3a,12a-Dihydroxy-5b-cholanate; 3alpha,12alpha-Dihydroxy-5beta-cholanate; 3alpha,12alpha-Dihydroxy-5beta-cholanic acid; 3beta-Isomer deoxycholic acid; 5alpha-Isomer deoxycholic acid; 5b-Cholanic acid-3a,12a-diol; 5b-Deoxycholate; 5b-Deoxycholic acid; 7-Deoxycholate; 7-Deoxycholic acid; 7a-Deoxycholate; 7a-Deoxycholic acid; 7alpha-Deoxycholic acid; Acid, 5alpha-isomer deoxycholic; Acid, choleic; Acid, deoxycholic; Acid, desoxycholic; Acid, dihydroxycholanoic; Acid, lagodeoxycholic; Choleic acid; Cholerebic; Cholorebic; Degalol; Deoxy-cholate; Deoxy-cholic acid; Deoxycholatate; Deoxycholate; Deoxycholate, sodium; Deoxycholatic acid; Deoxycholic acid, 12beta isomer; Deoxycholic acid, 12beta-isomer; Deoxycholic acid, 3beta isomer; Deoxycholic acid, 3beta-isomer; Deoxycholic acid, 5alpha isomer; Deoxycholic acid, 5alpha-isomer; Deoxycholic acid, disodium salt; Deoxycholic acid, magnesium (2:1) salt; Deoxycholic acid, monoammonium salt; Deoxycholic acid, monopotassium salt; Deoxycholic acid, monosodium salt; Deoxycholic acid, sodium salt, 12beta-isomer; Desoxycholate; Desoxycholic acid; Desoxycholsaeure; Dihydroxycholanoic acid; Lagodeoxycholic acid; Sodium deoxycholate
|
| Function |
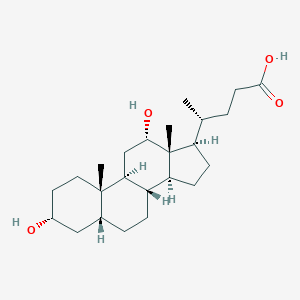
Deoxycholic acid is a secondary bile acid produced in the liver and is usually conjugated with glycine or taurine. It facilitates fat absorption and cholesterol excretion. Bile acids are steroid acids found predominantly in the bile of mammals. The distinction between different bile acids is minute, and depends only on the presence or absence of hydroxyl groups on positions 3, 7, and 12. Bile acids are physiological detergents that facilitate excretion, absorption, and transport of fats and sterols in the intestine and liver. Bile acids are also steroidal amphipathic molecules derived from the catabolism of cholesterol. They modulate bile flow and lipid secretion, are essential for the absorption of dietary fats and vitamins, and have been implicated in the regulation of all the key enzymes involved in cholesterol homeostasis. Bile acids recirculate through the liver, bile ducts, small intestine, and portal vein to form an enterohepatic circuit. They exist as anions at physiological pH, and consequently require a carrier for transport across the membranes of the enterohepatic tissues. The unique detergent properties of bile acids are essential for the digestion and intestinal absorption of hydrophobic nutrients. Bile acids have potent toxic properties (e.g. membrane disruption) and there are a plethora of mechanisms to limit their accumulation in blood and tissues. When present in sufficiently high levels, deoxycholic acid can act as a hepatotoxin, a metabotoxin, and an oncometabolite. A hepatotoxin causes damage to the liver or liver cells. A metabotoxin is an endogenously produced metabolite that causes adverse health effects at chronically high levels. An oncometabolite is a compound, when present at chronically high levels, that promotes tumour growth and survival. Among the primary bile acids, cholic acid is considered to be the least hepatotoxic while deoxycholic acid is the most hepatoxic. The liver toxicity of bile acids appears to be due to their ability to peroxidate lipids and to lyse liver cells. High bile acid levels lead to the generation of reactive oxygen species and reactive nitrogen species, disruption of the cell membrane and mitochondria, induction of DNA damage, mutation and apoptosis, and the development of reduced apoptosis capability upon chronic exposure. Chronically high levels of deoxycholic acid are associated with familial hypercholanemia. In hypercholanemia, bile acids, including deoxycholic acid, are elevated in the blood. This disease causes liver damage, extensive itching, poor fat absorption, and can lead to rickets due to lack of calcium in bones. The deficiency of normal bile acids in the intestines results in a deficiency of vitamin K, which also adversely affects clotting of the blood. The bile acid ursodiol (ursodeoxycholic acid) can improve symptoms associated with familial hypercholanemia. Chronically high levels of deoxycholic acid are also associated with several forms of cancer including colon cancer, pancreatic cancer, esophageal cancer, and many other GI cancers.
|
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair