| General Information of MET (ID: META00231) |
| Name |
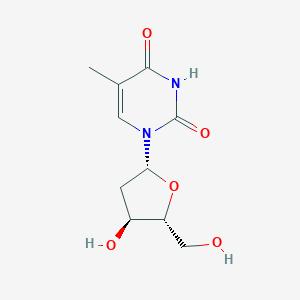
Thymidine
|
| Synonyms |
Click to Show/Hide Synonyms of This Metabolite
1-(2-Deoxy-b-D-erythro-pentofuranosyl)-5-methyl-2,4(1H,3H)-pyrimidinedione; 1-(2-Deoxy-beta-D-erythro-pentofuranosyl)-5-methylpyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione', 2'-Deoxy-5-methyluridine, 2'-Deoxythymidine, 2'-Thymidine, 5-Methyl-2'-deoxyuridine, 'Deoxythymidine; 1-(2-Deoxy-beta-delta-erythro-pentofuranosyl)-5-methyl-2,4(1H,3H)-pyrimidinedione; 1-[4-Hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]-5-methyl-pyrimidine-2,4-dione', 2'-Deoxy-5-methyl-uridine, '5-Methyldeoxyuridine; DT; DTHD; DThyd; Deoxyribothymidine; Thymidin; Thymine 2-desoxyriboside; Thymine deoxyriboside; Thymine-1 2-deoxy-b-D-ribofuranoside; Thymine-1 2-deoxy-beta-delta-ribofuranoside', 2' Deoxythymidine
|
| Source |
Endogenous;Escherichia Coli Metabolite;Yeast Metabolite;Food;Cosmetic;TCM Ingredients;Microbial
|
| Structure Type |
Pyrimidine 2'-deoxyribonucleosides (Click to Show/Hide the Complete Structure Type Hierarchy)
Nucleosides, nucleotides, and analogues
Pyrimidine nucleosides
Pyrimidine 2'-deoxyribonucleosides
|
| PubChem CID |
|
| HMDB ID |
|
| Formula |
C10H14N2O5
|
| Structure |
<iframe style="width: 300px; height: 300px;" frameborder="0" src="https://embed.molview.org/v1/?mode=balls&cid=5789"></iframe>
|
 |
|
3D MOL
|
2D MOL
|
|
Click to Show/Hide the Molecular/Functional Data (External Links/Property/Function) of This Metabolite
|
| KEGG ID |
|
| DrugBank ID |
|
| ChEBI ID |
|
| FooDB ID |
|
| ChemSpider ID |
|
| METLIN ID |
|
| Physicochemical Properties |
Molecular Weight |
242.23 |
Topological Polar Surface Area |
99.1 |
| XlogP |
-1.2 |
Complexity |
381 |
| Heavy Atom Count |
17 |
Rotatable Bond Count |
2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
3 |
Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
5 |
| Function |
Thymidine, also known as deoxythymidine or DTHD, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as pyrimidine 2'-deoxyribonucleosides. Pyrimidine 2'-deoxyribonucleosides are compounds consisting of a pyrimidine linked to a ribose which lacks a hydroxyl group at position 2. Thymidine is an extremely weak basic (essentially neutral) compound (based on its pKa). Thymidine exists in all living species, ranging from bacteria to humans. In cell biology, it is used to synchronize the cells in S phase. Within humans, thymidine participates in a number of enzymatic reactions. In particular, thymidine can be biosynthesized from 5-thymidylic acid through its interaction with the enzyme cytosolic purine 5'-nucleotidase. In addition, thymidine can be converted into 5-thymidylic acid; which is catalyzed by the enzyme thymidine kinase. In humans, thymidine is involved in the metabolic disorder called UMP synthase deficiency (orotic aciduria). Outside of the human body, thymidine has been detected, but not quantified in, several different foods, such as horned melons, Asian pears, brassicas, Japanese chestnuts, and apricots. This could make thymidine a potential biomarker for the consumption of these foods. Thymidine is non-toxic and is a naturally occurring compound that exists in all living organisms and DNA viruses. 25% of DNA is composed of thymidine. RNA does not have thymidine and has uridine instead. Thymidine is the DNA nucleoside T, which pairs with adenosine (A) in double-stranded DNA.
|
|
Regulatory Network
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair

