|
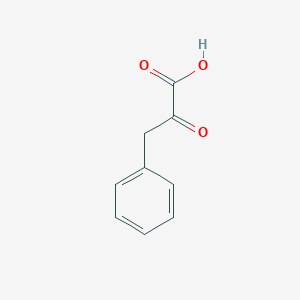
Phenylpyruvic acid is a keto-acid that is an intermediate or catabolic byproduct of phenylalanine metabolism. It has a slight honey-like odor. Levels of phenylpyruvate are normally very low in blood or urine. High levels of phenylpyruvic acid can be found in the urine of individuals with phenylketonuria (PKU), an inborn error of metabolism. PKU is due to lack of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH), so that phenylalanine is converted not to tyrosine but to phenylpyruvic acid. In particular, excessive phenylalanine can be metabolized into phenylketones through, a transaminase pathway route involving glutamate. Metabolites of this transamination reaction include phenylacetate, phenylpyruvate and phenethylamine. In persons with PKU, dietary phenylalanine either accumulates in the body or some of it is converted to phenylpyruvic acid. Individuals with PKU tend to excrete large quantities of phenylpyruvate, phenylacetate and phenyllactate, along with phenylalanine, in their urine. If untreated, mental retardation effects and microcephaly are evident by the first year along with other symptoms which include: unusual irritability, epileptic seizures and skin lesions. Hyperactivity, EEG abnormalities and seizures, and severe learning disabilities are major clinical problems later in life. A "musty or mousy" odor of skin, hair, sweat and urine (due to phenylacetate accumulation); and a tendency to hypopigmentation and eczema are also observed. The neural-development effects of PKU are primarily due to the disruption of neurotransmitter synthesis. In particular, phenylalanine is a large, neutral amino acid which moves across the blood-brain barrier (BBB) via the large neutral amino acid transporter (LNAAT). Excessive phenylalanine in the blood saturates the transporter. Thus, excessive levels of phenylalanine significantly decrease the levels of other LNAAs in the brain. But since these amino acids are required for protein and neurotransmitter synthesis, phenylalanine accumulation disrupts brain development, leading to mental retardation. Phenylpyruvic acid is also a microbial metabolite, it can be produced by Lactobacillus plantarum.
|
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair