| General Information of MET (ID: META00164) |
| Name |
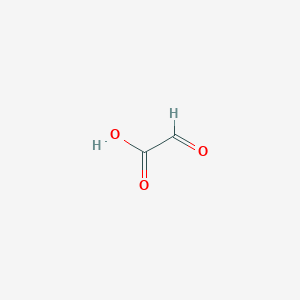
Glyoxylic acid
|
| Synonyms |
Click to Show/Hide Synonyms of This Metabolite
Formylformate; Formylformic acid; Glyoxalate; Glyoxalic acid; Glyoxalsaeure; Glyoxylate; Glyoxylic acid, 14c2-labeled; Glyoxylic acid, 2-(14)C-labeled; Glyoxylic acid, calcium salt; Glyoxylic acid, sodium salt; Glyoxylic acid, sodium salt, 14C-labeled; Glyoxylic acid, sodium salt, 2-(14)C-labeled; Glyoxylsaeure; Oxalaldehydate; Oxalaldehydic acid; Oxoacetate; Oxoacetic acid; Oxoethanoate; Oxoethanoic acid; a-Ketoacetate; a-Ketoacetic acid; alpha-Ketoacetic acid
|
| Source |
Endogenous;Escherichia Coli Metabolite;Yeast Metabolite;Food;Drug;Cosmetic;Microbial
|
| Structure Type |
Carboxylic acids (Click to Show/Hide the Complete Structure Type Hierarchy)
Organic acids and derivatives
Carboxylic acids and derivatives
Carboxylic acids
|
| PubChem CID |
|
| HMDB ID |
|
| Formula |
C2H2O3
|
| Structure |
<iframe style="width: 300px; height: 300px;" frameborder="0" src="https://embed.molview.org/v1/?mode=balls&cid=760"></iframe>
|
 |
|
3D MOL
|
2D MOL
|
|
Click to Show/Hide the Molecular/Functional Data (External Links/Property/Function) of This Metabolite
|
| KEGG ID |
|
| DrugBank ID |
|
| ChEBI ID |
|
| FooDB ID |
|
| ChemSpider ID |
|
| METLIN ID |
|
| Physicochemical Properties |
Molecular Weight |
74.04 |
Topological Polar Surface Area |
54.4 |
| XlogP |
-0.3 |
Complexity |
55.9 |
| Heavy Atom Count |
5 |
Rotatable Bond Count |
1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
1 |
Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
3 |
| Function |
Glyoxylic acid or oxoacetic acid is an organic compound that is both an aldehyde and a carboxylic acid. Glyoxylic acid is a liquid with a melting point of -93C and a boiling point of 111C. It is an intermediate of the glyoxylate cycle, which enables certain organisms to convert fatty acids into carbohydrates. The conjugate base of glyoxylic acid is known as glyoxylate. In humans, glyoxylate is produced via two pathways: (1) through the oxidation of glycolate in peroxisomes and (2) through the catabolism of hydroxyproline in mitochondria. In the peroxisomes, glyoxylate is converted into glycine by glyoxylate aminotransferase (AGT1) or into oxalate by glycolate oxidase. In the mitochondria, glyoxylate is converted into glycine by mitochondrial glyoxylate aminotransferase AGT2 or into glycolate by glycolate reductase. A small amount of glyoxylate is converted into oxalate by cytoplasmic lactate dehydrogenase. Glyoxylic acid is found to be associated with primary hyperoxaluria I, which is an inborn error of metabolism. Under certain circumstances, glyoxylate can be a nephrotoxin and a metabotoxin. A nephrotoxin is a compound that causes damage to the kidney and kidney tissues. A metabotoxin is an endogenously produced metabolite that causes adverse health effects at chronically high levels. High levels of glyoxylate are involved in the development of hyperoxaluria, a key cause of nephrolithiasis (commonly known as kidney stones). Glyoxylate is both a substrate and inductor of sulfate anion transporter-1 (SAT-1), a gene responsible for oxalate transportation, allowing it to increase SAT-1 mRNA expression, and as a result oxalate efflux from the cell. The increased oxalate release allows the buildup of calcium oxalate in the urine, and thus the eventual formation of kidney stones. As an aldehyde, glyoxylate is also highly reactive and will modify proteins to form advanced glycation products (AGEs).
|
|
Regulatory Network
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair

