| General Information of MET (ID: META00140) |
| Name |
Cellobiose
|
| Synonyms |
Click to Show/Hide Synonyms of This Metabolite
1-beta-D-Glucopyranosyl-4-beta-D-glucopyranose; 4 O beta D Glucopyranosyl D glucopyranose; 4-(b-D-Glucosido)-D-glucose; 4-(b-delta-Glucosido)-delta-glucose; 4-(beta-D-Glucosido)-D-glucose; 4-(beta-delta-Glucosido)-delta-glucose; 4-O-b-D-Glucopyranosyl-D-glucose; 4-O-beta-D-Glucopyranosyl-D-glucopyranose; 4-O-beta-D-Glucopyranosyl-D-glucose; 4-O-beta-D-Glucopyranosyl-beta-D-glucopyranose; 4-O-beta-delta-Glucopyranosyl-delta-glucose; 4-beta-D-Glucopyranosyl-D-glucopyranose; 4-beta-delta-Glucopyranosyl-delta-glucopyranose; CELLOBIOSE; Cellose; D-(+)-Cellobiose; D-Cellobiose; D-Glucosyl-b-(1->4)-D-glucose; D-Glucosyl-beta-(1-4)-D-glucose; D-Glucosyl-beta-(1->4)-D-glucose; GLCB1-4GLCB; Glcbeta1-4glcbeta; beta-D-GLC-(1->4)-beta-D-GLC; beta-D-GLCP-(1->4)-beta-D-GLCP; beta-D-Glucosyl-(1->4)-beta-D-glucose; delta-(+)-Cellobiose; delta-Cellobiose; delta-Glucosyl-beta-(1-4)-delta-glucose; delta-Glucosyl-beta-(1->4)-delta-glucose
|
| Source |
Food;Escherichia Coli Metabolite;Yeast Metabolite;Food;Microbial
|
| Structure Type |
Carbohydrates and carbohydrate conjugates (Click to Show/Hide the Complete Structure Type Hierarchy)
Organic oxygen compounds
Organooxygen compounds
Carbohydrates and carbohydrate conjugates
|
| PubChem CID |
|
| HMDB ID |
|
| Formula |
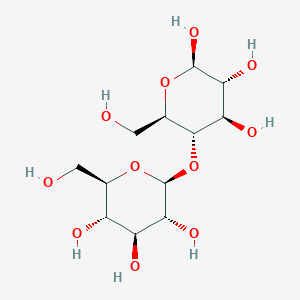
C12H22O11
|
| Structure |
<iframe style="width: 300px; height: 300px;" frameborder="0" src="https://embed.molview.org/v1/?mode=balls&cid=10712"></iframe>
|
 |
|
3D MOL
|
2D MOL
|
|
Click to Show/Hide the Molecular/Functional Data (External Links/Property/Function) of This Metabolite
|
| KEGG ID |
|
| ChEBI ID |
|
| FooDB ID |
|
| ChemSpider ID |
|
| METLIN ID |
|
| Physicochemical Properties |
Molecular Weight |
342.3 |
Topological Polar Surface Area |
190 |
| XlogP |
-4.7 |
Complexity |
382 |
| Heavy Atom Count |
23 |
Rotatable Bond Count |
4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
8 |
Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
11 |
| Function |
Cellobiose is a disaccharide consisting of two glucose units in a beta (1-4) glycosidic linkage. Obtained from the partial hydrolysis of cellulose, cellobiose is commonly used as an indicator carbohydrate for intestinal permeability in Crohn's disease and malabsorption syndrome. This carbohydrate is exogenous and is a microbial breakdown product from plant material (cellulose). It is not produced by the body nor is it readily metabolized by the body, but may be found in some food products (vegetables, fruits, corn syrups, etc.). Recent studies have shown that cellobiose can be processed or metabolized by endogenous beta glycosidases in the mammalian small intestine. Cellobiose is also a microbe metabolite.
|
|
Regulatory Network
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair

