|
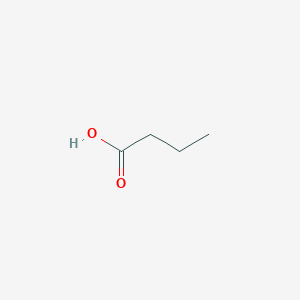
Butyric acid, a four-carbon fatty acid, is formed in the human colon by bacterial fermentation of carbohydrates (including dietary fiber), and putatively suppresses colorectal cancer (CRC). Butyrate has diverse and apparently paradoxical effects on cellular proliferation, apoptosis and differentiation that may be either pro-neoplastic or anti-neoplastic, depending upon factors such as the level of exposure, availability of other metabolic substrate and the intracellular milieu. In humans, the relationship between luminal butyrate exposure and CRC has been examined only indirectly in case-control studies, by measuring fecal butyrate concentrations, although this may not accurately reflect effective butyrate exposure during carcinogenesis. Perhaps not surprisingly, results of these investigations have been mutually contradictory. The direct effect of butyrate on tumorigenesis has been assessed in a no. of in vivo animal models, which have also yielded conflicting results. In part, this may be explained by methodology: differences in the amount and route of butyrate administration, which are likely to significantly influence delivery of butyrate to the distal colon. Butyric acid is a carboxylic acid found in rancid butter, parmesan cheese, and vomit, and has an unpleasant odor and acrid taste, with a sweetish aftertaste (similar to ether). Butyric acid is a fatty acid occurring in the form of esters in animal fats and plant oils. Interestingly, low-molecular-weight esters of butyric acid, such as methyl butyrate, have mostly pleasant aromas or tastes. As a consequence, they find use as food and perfume additives. Butyrate is produced as end-product of a fermentation process solely performed by obligate anaerobic bacteria. It is a metabololite of Anaerostipes, Coprococcus, Eubacterium, Faecalibacterium and Roseburia.
|
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair