| General Information of MET (ID: META00007) |
| Name |
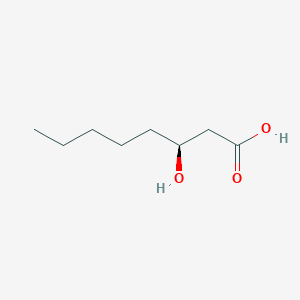
3-Hydroxyoctanoic acid
|
| Synonyms |
Click to Show/Hide Synonyms of This Metabolite
(3S)-3-Hydroxy-octanoate; (3S)-3-Hydroxy-octanoic acid; (3S)-3-Hydroxyoctanoate; (S)-3-Hydroxycaprylate; (S)-3-Hydroxycaprylic acid; (S)-3-Hydroxyoctanoate; (S)-3-OH Octanoate; (S)-3-OH Octanoic acid; (S)-3-OH-Caprylate; (S)-3-OH-Caprylic acid; (S)-b-Hydroxycaprylate; (S)-b-Hydroxycaprylic acid; (S)-b-Hydroxyoctanoate; (S)-b-Hydroxyoctanoic acid; (S)-b-OH-Caprylate; (S)-b-OH-Caprylic acid; (S)-b-OH-Octanoate; (S)-b-OH-Octanoic acid; (S)-beta-Hydroxycaprylic acid; (S)-beta-Hydroxyoctanoic acid; (S)-beta-OH-Caprylic acid; (S)-beta-OH-Octanoic acid; 3-Hydroxycaprylate; 3-Hydroxycaprylic acid; 3-Hydroxyoctanoate; 3-Hydroxyoctanoic acid; 3-Hydroxyoctanoic acid, (S)-isomer; FA(8:0(3-OH)); FA(8:0(3S-OH)); S-3-Hydroxyoctanoate; S-3-Hydroxyoctanoic acid; beta-Hydroxycaprylate; beta-Hydroxycaprylic acid; beta-Hydroxyoctanoate
|
| Source |
Endogenous;Fatty acyls;Food
|
| Structure Type |
Medium-chain hydroxy acids and derivatives (Click to Show/Hide the Complete Structure Type Hierarchy)
Organic acids and derivatives
Hydroxy acids and derivatives
Medium-chain hydroxy acids and derivatives
|
| PubChem CID |
|
| HMDB ID |
|
| Formula |
C8H16O3
|
| Structure |
<iframe style="width: 300px; height: 300px;" frameborder="0" src="https://embed.molview.org/v1/?mode=balls&cid=11367166"></iframe>
|
 |
|
3D MOL
|
2D MOL
|
|
Click to Show/Hide the Molecular/Functional Data (External Links/Property/Function) of This Metabolite
|
| ChEBI ID |
|
| FooDB ID |
|
| ChemSpider ID |
|
| Physicochemical Properties |
Molecular Weight |
160.21 |
Topological Polar Surface Area |
57.5 |
| XlogP |
1.4 |
Complexity |
112 |
| Heavy Atom Count |
11 |
Rotatable Bond Count |
6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
2 |
Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
3 |
| Function |
3-Hydroxyoctanoic acid (CAS: 14292-27-4) is an organic 3-hydroxy dicarboxylic acid, a metabolite of medium-chain fatty acid oxidation found in human urine. It is believed that urinary 3-hydroxy dicarboxylic acids are derived from the omega-oxidation of 3-hydroxy fatty acids and the subsequent beta-oxidation of longer-chain 3-hydroxy dicarboxylic acids. 3-Hydroxyoctanoic acid has been identified in the human placenta.
|
|
Regulatory Network
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair

