| Synonyms |
Click to Show/Hide Synonyms of This Metabolite
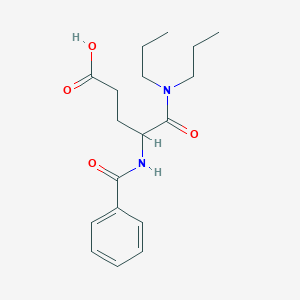
6620-60-6; 4-benzamido-5-(dipropylamino)-5-oxopentanoic acid; Proglumidum; Proglumida; Pentanoic acid, 4-(benzoylamino)-5-(dipropylamino)-5-oxo-; W-5219; (+-)-4-Benzamido-N,N-dipropylglutaramic acid; Binoside; Xylamide; Nulsa; Pentanoic acid, 4-(benzoylamino)-5-(dipropylamino)-5-oxo-, (+-)-; CHEMBL316561; CHEBI:32058; dl-proglumide; Milid; 4-(benzoylamino)-5-(dipropylamino)-5-oxopentanoic acid; Gastrotopic; Midelid; Ulcutin; Milide; Xyde; DSSTox_CID_3516; DSSTox_RID_77060
|
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair