| Synonyms |
Click to Show/Hide Synonyms of This Metabolite
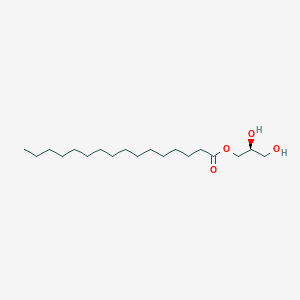
(+-)-2,3-Dihydroxypropyl hexadecanoate; (1)-2,3-Dihydroxypropyl palmitate; (2S)-1-O-Hexadecanoylglycerol; (2S)-1-O-Palmitoylglycerol; (C16-C22)Trialkyl glyceride; (S)-1-Monopalmitin; (S)-2,3-Dihydroxypropyl N-hexadecanoate; (S)-2,3-Dihydroxypropyl N-hexadecanoic acid; (S)-2,3-Dihydroxypropyl palmitate; 1,2,3-Propanetriol 1-hexandecanoyl ester; 1-Glycerol hexadecanoates; 1-Glyceryl hexadecanoate; 1-Glyceryl monohexadecanoate; 1-Hexadecanoyl-sn-glycerol; 1-Hexadecanoylglycerol; 1-MONOPALMITOYL-rac-glycerol; 1-Monohexadecanoyl-rac-glycerol; 1-Monohexadecanoylglycerol; 1-Monopalmitin; 1-Monopalmitoylglycerol; 1-O-Hexadecanoylglycerol; 1-O-Palmitoyl-DL-glycerol; 1-O-Palmitoylglycerol; 1-Palmitoyl-rac-glycerol; 1-Palmitoylglycerol; 1-mono-Palmitin; 2,3-Dihydroxypropyl ester(.+/-.)-hexadecanoic acid; 2,3-Dihydroxypropyl hexadecanoate; 2,3-Dihydroxypropyl hexadecanoic acid; 2,3-Dihydroxypropyl palmitate; DL-1-Monopalmitin; DL-alpha-Palmitin; Glycerol 1-hexadecanoic acid; Glycerol 1-monohexadecanoate; Glycerol 1-monopalmitate; Glycerol 1-monopalmitic acid; Glycerol 1-palmitate; Glycerol 1-palmitic acid; Glycerol 3-palmitate; Glycerol 3-palmitic acid; Glycerol alpha -palmitate; Glycerol palmitate; Glyceryl monopalmitate; Glyceryl palmitate; Glyceryl palmitic acid; Hexadecanoate, 2,3-dihydroxypropyl ester; Hexadecanoic acid, 2,3-bishydroxy propyl ester; Hexadecanoic acid, 2,3-dihydroxypropyl ester; Hexadexanoic acid 2,3-dihydroxypropyl ester; L-(-)-alpha-Monopalmitin; MG (16:0/0:0/0:0); Monopalmitin; Palmitate a-monoglyceride; Palmitic acid alpha -monoglyceride; Palmitic acid alpha-monoglyceride; Palmitin, 1-mono; Palmitin, 1-mono- (8ci); Palmitoyl glycerol; Palmitoyl glycerol, (+,-)-isomer; Palmitoyl glycerol, hexadecanoic-1-(14)C-labeled CPD, (R)-isomer; alpha -Monopalmitin; alpha-Monopalmitin; rac-1(3)-Palmitoyl glycerol; rac-1-Palmitoylglycerol; rac-Glycerol 1-palmitate; sn-1-Palmitoylmonoglyceride; sn-1-Palmitoylmonoglycerol
|
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair