| General Information of MET (ID: META00859) |
| Name |
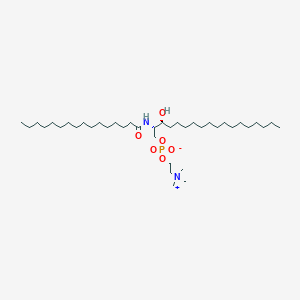
Sphingomyelin (d18:0/16:0)
|
| Synonyms |
Click to Show/Hide Synonyms of This Metabolite
(2S,3R)-3-Hydroxy-2-(palmitoylamino)octadecyl 2-(trimethylazaniumyl)ethyl phosphate; (2S,3R)-3-Hydroxy-2-(palmitoylamino)octadecyl 2-(trimethylazaniumyl)ethyl phosphoric acid; 16:0 Dihydrosphingomyelin; C16 Dihydrosphingomyelin; C16-Dihydrosphingomyelin; Dihydrosphingomyelin C16:0; N-(Hexadecanoyl)-1-phosphocholine-D-erythro-sphinganine; N-(Hexadecanoyl)-1-phosphocholine-dihydrosphingosine; N-(Hexadecanoyl)-1-phosphocholine-sphinganine; N-(Hexadecanoyl)-sphinganine-1-phosphocholine; N-Hexadecanoyl-sphinganine-1-phosphocholine; N-Hexadecanoyldihydroceramide-1-phosphocholine; N-Palmitoyldihydroceramide-1-phosphocholine; N-Palmitoyldihydrosphingomyelin; N-Palmitoylsphinganine-1-phosphocholine; Palmitoyl dihydrosphingomyelin; Palmitoyl dihydrosphingomyelin (d18:0/16:0); Palmitoyldihydrosphingomyelin; SM d18:0/16:0; SM(18:0/16:0); SM(d18:0/16:0); Sphingomyelin; Sphingomyelin (d18:0,C16:0); Sphingomyelin (d18:0/16:0); Sphingomyelin(d18:0/16:0); {[(2S,3R)-2-hexadecanamido-3-hydroxyoctadecyl]oxy}[2-(trimethylazaniumyl)ethoxy]phosphinate; {[(2S,3R)-2-hexadecanamido-3-hydroxyoctadecyl]oxy}[2-(trimethylazaniumyl)ethoxy]phosphinic acid
|
| Source |
Aliphatic acyclic compounds
|
| Structure Type |
Phosphosphingolipids (Click to Show/Hide the Complete Structure Type Hierarchy)
Lipids and lipid-like molecules
Sphingolipids
Phosphosphingolipids
|
| PubChem CID |
|
| HMDB ID |
|
| Formula |
C39H81N2O6P
|
| Structure |
<iframe style="width: 300px; height: 300px;" frameborder="0" src="https://embed.molview.org/v1/?mode=balls&cid=9939965"></iframe>
|
 |
|
3D MOL is unavailable
|
2D MOL
|
|
Click to Show/Hide the Molecular/Functional Data (External Links/Property/Function) of This Metabolite
|
| ChEBI ID |
|
| FooDB ID |
|
| ChemSpider ID |
|
| Physicochemical Properties |
Molecular Weight |
705 |
Topological Polar Surface Area |
108 |
| XlogP |
12.8 |
Complexity |
755 |
| Heavy Atom Count |
48 |
Rotatable Bond Count |
37 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
2 |
Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
6 |
| Function |
Sphingomyelin (d18:0/16:0) or SM(d18:0/16:0) is a type of sphingolipid found in animal cell membranes, especially in the membranous myelin sheath which surrounds some nerve cell axons. It usually consists of phosphorylcholine and ceramide. SM(d18:0/16:0) consists of a sphinganine backbone and a palmitic acid chain. In humans, sphingomyelin is the only membrane phospholipid not derived from glycerol. Like all sphingolipids, SM has a ceramide core (sphingosine bonded to a fatty acid via an amide linkage). In addition, it contains one polar head group, which is either phosphocholine or phosphoethanolamine. The plasma membrane of cells is highly enriched in sphingomyelin and is considered largely to be found in the exoplasmic leaflet of the cell membrane. However, there is some evidence that there may also be a sphingomyelin pool in the inner leaflet of the membrane. Moreover, neutral sphingomyelinase-2, an enzyme that breaks down sphingomyelin into ceramide, has been found to localize exclusively to the inner leaflet further suggesting that there may be sphingomyelin present there. Sphingomyelin can accumulate in a rare hereditary disease called Niemann-Pick Disease, types A and B. Niemann-Pick disease is a genetically-inherited disease caused by a deficiency in the enzyme sphingomyelinase, which causes the accumulation of sphingomyelin in spleen, liver, lungs, bone marrow, and the brain, causing irreversible neurological damage. SMs play a role in signal transduction. Sphingomyelins are synthesized by the transfer of phosphorylcholine from phosphatidylcholine to a ceramide in a reaction catalyzed by sphingomyelin synthase.
|
|
Regulatory Network
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair

