| General Information of MET (ID: META00856) |
| Name |
Gamma-Glutamylalanine
|
| Synonyms |
Click to Show/Hide Synonyms of This Metabolite
5-L-Glutamyl-L-alanine; 5-L-Glutamylalanine; L-gamma-Glu-L-ala; L-gamma-Glutamyl-L-alanine; N-L-g-Glutamyl-L-alanine; N-L-gamma-Glutamyl-L-alanine; N-L-gamma-Glutamylalanine; N-gamma-Glutamylalanine; N-gamma-L-Glutamyl-L-alanine; g-Glutamylalanine; g-L-Glutamyl-L-alanine; gamma-Glu-Ala; gamma-Glutamylalanine; gamma-L-Glu-L-Ala; gamma-L-Glutamyl-L-alanine
|
| Source |
Endogenous;Yeast Metabolite;Food;Microbial
|
| Structure Type |
Amino acids, peptides, and analogues (Click to Show/Hide the Complete Structure Type Hierarchy)
Organic acids and derivatives
Carboxylic acids and derivatives
Amino acids, peptides, and analogues
|
| PubChem CID |
|
| HMDB ID |
|
| Formula |
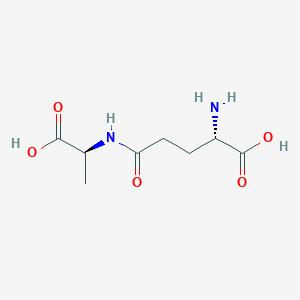
C8H14N2O5
|
| Structure |
<iframe style="width: 300px; height: 300px;" frameborder="0" src="https://embed.molview.org/v1/?mode=balls&cid=440103"></iframe>
|
 |
|
3D MOL
|
2D MOL
|
|
Click to Show/Hide the Molecular/Functional Data (External Links/Property/Function) of This Metabolite
|
| KEGG ID |
|
| ChEBI ID |
|
| FooDB ID |
|
| ChemSpider ID |
|
| Physicochemical Properties |
Molecular Weight |
218.21 |
Topological Polar Surface Area |
130 |
| XlogP |
-3.8 |
Complexity |
266 |
| Heavy Atom Count |
15 |
Rotatable Bond Count |
6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
4 |
Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
6 |
| Function |
gamma-Glutamylalanine is a dipeptide composed of gamma-glutamate and alanine, and is a proteolytic breakdown product of larger proteins. It belongs to the family of N-acyl-alpha amino acids and derivatives. These are compounds containing an alpha amino acid which bears an acyl group at its terminal nitrogen atom. gamma-Glutamylalanine is a natural substrate of the enzyme (5-L-glutamyl)-L-amino acid 5-glutamyltransferase (cyclizing) (g-glutamylcyclotransferase, EC 2.3.2.2) in the glutathione metabolism pathway, which cleaves gamma-glutamylalanine to produce L-5-oxoproline. gamma-Glutamylcyclotransferase is widely distributed in both human and animal tissues where it catalyzes the scission of the y-peptide bonds of many different gamma-glutamyl-amino acids and gamma-glutamyl-gamma-glutamyl-amino acids. The latter are 'better' substrates of the enzyme than the corresponding gamma-glutamyl-amino acids.
|
|
Regulatory Network
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair

