| General Information of MET (ID: META00855) |
| Name |
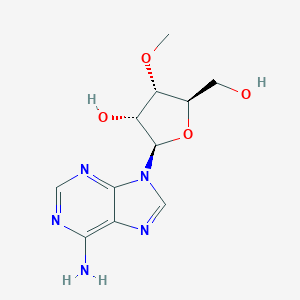
3'-O-Methyladenosine
|
| Synonyms |
Click to Show/Hide Synonyms of This Metabolite
3'-O-Methyl-adenosine, 3'-O-Methyladenosine
|
| Source |
Endogenous;Food
|
| Structure Type |
Purine nucleosides (Click to Show/Hide the Complete Structure Type Hierarchy)
Nucleosides, nucleotides, and analogues
Purine nucleosides
|
| PubChem CID |
|
| HMDB ID |
|
| Formula |
C11H15N5O4
|
| Structure |
<iframe style="width: 300px; height: 300px;" frameborder="0" src="https://embed.molview.org/v1/?mode=balls&cid=82530"></iframe>
|
 |
|
3D MOL
|
2D MOL
|
|
Click to Show/Hide the Molecular/Functional Data (External Links/Property/Function) of This Metabolite
|
| FooDB ID |
|
| ChemSpider ID |
|
| Physicochemical Properties |
Molecular Weight |
281.27 |
Topological Polar Surface Area |
129 |
| XlogP |
-1.1 |
Complexity |
349 |
| Heavy Atom Count |
20 |
Rotatable Bond Count |
3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
3 |
Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
8 |
| Function |
3-O-Methyladenosine is a methylated adenine residue.
|
|
Regulatory Network
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair

