| General Information of MET (ID: META00844) |
| Name |
Epsilon-(gamma-Glutamyl)lysine
|
| Synonyms |
Click to Show/Hide Synonyms of This Metabolite
Epsilon-(g-Glutamyl)-lysine; GGEL peptide; L-g-Glutamyl-L-epsilon-lysine; L-gamma-Glutamyl-L-epsilon-lysine; N(6)-L-g-Glutamyl-L-lysine; N(6)-L-gamma-Glutamyl-L-lysine; N(epsilon)-(g-Glutamyl)-lysine; N(epsilon)-(gamma-Glutamyl)-lysine; N-epsilon-(gamma-L-Glutamyl)lysine; Nepsilon(gamma-Glutamyl)lysine; epsilon-(L-g-Glutamyl)-L-lysine; epsilon-(L-gamma-Glutamyl)-L-lysine; epsilon-(g-Glutamyl)lysine; epsilon-(g-L-Glutamyl)-L-lysine; epsilon-(gamma-Glu)-lys; epsilon-(gamma-Glutamyl)-lysine; epsilon-(gamma-Glutamyl)lysine; epsilon-(gamma-Glutamyl)lysine isodipeptide; epsilon-(gamma-L-Glutamyl)-L-lysine; epsilon-(gamma-L-Glutamyl)lysine; g-Glu-epsilon-lys; g-Glutamyl-epsilon-lysine; gamma-Glu-epsilon-lys; gamma-Glutamyl-epsilon-lysine
|
| Source |
Endogenous;Food
|
| Structure Type |
Amino acids, peptides, and analogues (Click to Show/Hide the Complete Structure Type Hierarchy)
Organic acids and derivatives
Carboxylic acids and derivatives
Amino acids, peptides, and analogues
|
| PubChem CID |
|
| HMDB ID |
|
| Formula |
C11H21N3O5
|
| Structure |
<iframe style="width: 300px; height: 300px;" frameborder="0" src="https://embed.molview.org/v1/?mode=balls&cid=7015684"></iframe>
|
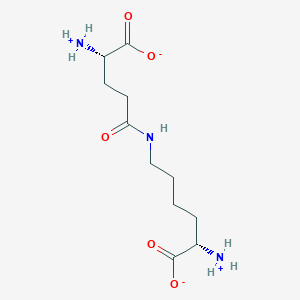 |
|
3D MOL
|
2D MOL
|
|
Click to Show/Hide the Molecular/Functional Data (External Links/Property/Function) of This Metabolite
|
| ChEBI ID |
|
| FooDB ID |
|
| ChemSpider ID |
|
| Physicochemical Properties |
Molecular Weight |
275.3 |
Topological Polar Surface Area |
165 |
| XlogP |
-5 |
Complexity |
310 |
| Heavy Atom Count |
19 |
Rotatable Bond Count |
8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
3 |
Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
5 |
| Function |
In non-diabetic kidney scarring the protein crosslinking enzyme tissue transglutaminase (tTg) has been implicated in the process by the formation of increased epsilon-(gamma-glutamyl)lysine bonds between ECM components in both experimental and human disease. Changes in tTg and epsilon-(gamma-glutamyl)lysine occur in human Diabetic nephropathy as well, the leading cause of chronic kidney failure. In Parkinson's disease (PD), conformational changes in the alpha-synuclein monomer precede the formation of Lewy bodies. Both tTG and its substrate-characteristic N(epsilon)-(gamma-glutamyl)-lysine crosslink are increased in PD nigral dopamine neurons. Expression of tissue transglutaminase (tTgase) and epsilon-(gamma-glutamyl)-lysine was present in all scarring of the blebs sites, being the main cause of failure in glaucoma filtration surgery. Transglutaminases are calcium-dependent enzymes that catalyze the posttranslational modification of proteins through an acyl transfer reaction between the gamma-carboxamide group of a peptide-bound glutaminyl residue and various amines. Covalent cross-linking using epsilon-(gamma-glutamyl)-lysine bonds is stable and resistant to enzymatic, chemical, and mechanical disruption.
|
|
Regulatory Network
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair

