| General Information of MET (ID: META00837) |
| Name |
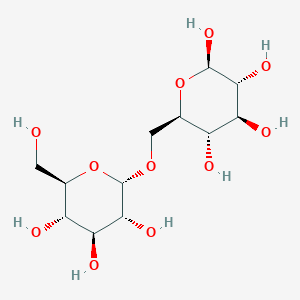
Isomaltose
|
| Synonyms |
Click to Show/Hide Synonyms of This Metabolite
6-O-alpha-D-Glucopyranosyl-D-glucose; D-Isomaltose; Isomaltose; beta-D-Isomaltose
|
| Source |
Endogenous;Escherichia Coli Metabolite;Yeast Metabolite;Food;Microbial
|
| Structure Type |
Carbohydrates and carbohydrate conjugates (Click to Show/Hide the Complete Structure Type Hierarchy)
Organic oxygen compounds
Organooxygen compounds
Carbohydrates and carbohydrate conjugates
|
| PubChem CID |
|
| HMDB ID |
|
| Formula |
C12H22O11
|
| Structure |
<iframe style="width: 300px; height: 300px;" frameborder="0" src="https://embed.molview.org/v1/?mode=balls&cid=10357"></iframe>
|
 |
|
3D MOL
|
2D MOL
|
|
Click to Show/Hide the Molecular/Functional Data (External Links/Property/Function) of This Metabolite
|
| Physicochemical Properties |
Molecular Weight |
342.3 |
Topological Polar Surface Area |
190 |
| XlogP |
-4.7 |
Complexity |
382 |
| Heavy Atom Count |
23 |
Rotatable Bond Count |
4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
8 |
Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
11 |
| Function |
Isomaltose (CAS: 499-40-1) is a naturally occurring disaccharide composed of two glucose units in an alpha (1-6) glycosidic linkage (PubChem). A deficiency of sucrase-isomaltase, an integral protein of the small intestine brush-border membrane responsible for catalyzing the hydrolysis of dietary sucrose and some of the products of starch digestion, results in osmotic diarrhea when the disaccharide is ingested because absorption cannot occur until after hydrolysis produces the component monosaccharides (OMIM: 222800). It is particularly suitable as a non-cariogenic sucrose replacement and is favourable in products for diabetics and prediabetic dispositions.
|
|
Regulatory Network
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair

