| General Information of MET (ID: META00797) |
| Name |
Acetylcholine
|
| Synonyms |
Click to Show/Hide Synonyms of This Metabolite
2-(Acetyloxy)-N,N,N-trimethylethanaminium; ACh; Acetilcolina cusi; Acetyl choline ion; Acetylcholine; Acetylcholine L tartrate; Acetylcholine L-tartrate; Acetylcholine bromide; Acetylcholine cation; Acetylcholine chloride; Acetylcholine fluoride; Acetylcholine hydroxide; Acetylcholine iodide; Acetylcholine perchlorate; Acetylcholine picrate; Acetylcholine picrate (1:1); Acetylcholine sulfate (1:1); Acetylcholinium: acetyl-choline; Alcon brand OF acetylcholine chloride; Azetylcholin; Bournonville brand OF acetylcholine chloride; Bromide, acetylcholine; Bromoacetylcholine; Chloroacetylcholine; Choline acetate; Choline acetate (ester); Choline acetic acid; Ciba vision brand OF acetylcholine chloride; Cusi, acetilcolina; Fluoride, acetylcholine; Hydroxide, acetylcholine; Iodide, acetylcholine; Iolab brand OF acetylcholine chloride; L-Tartrate, acetylcholine; Miochol; O-Acetylcholine; Perchlorate, acetylcholine
|
| Source |
Endogenous;Food;Drug;Cosmetic
|
| Structure Type |
Quaternary ammonium salts (Click to Show/Hide the Complete Structure Type Hierarchy)
Organic nitrogen compounds
Organonitrogen compounds
Quaternary ammonium salts
|
| PubChem CID |
|
| HMDB ID |
|
| Formula |
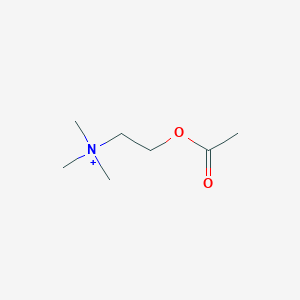
C7H16NO2
|
| Structure |
<iframe style="width: 300px; height: 300px;" frameborder="0" src="https://embed.molview.org/v1/?mode=balls&cid=187"></iframe>
|
 |
|
3D MOL
|
2D MOL
|
|
Click to Show/Hide the Molecular/Functional Data (External Links/Property/Function) of This Metabolite
|
| KEGG ID |
|
| DrugBank ID |
|
| ChEBI ID |
|
| FooDB ID |
|
| ChemSpider ID |
|
| METLIN ID |
|
| Physicochemical Properties |
Molecular Weight |
146.21 |
Topological Polar Surface Area |
26.3 |
| XlogP |
0.2 |
Complexity |
115 |
| Heavy Atom Count |
10 |
Rotatable Bond Count |
4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
N.A. |
Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
2 |
| Function |
Acetylcholine (ACh) is a neurotransmitter. Acetylcholine in vertebrates is the major transmitter at neuromuscular junctions, autonomic ganglia, parasympathetic effector junctions, a subset of sympathetic effector junctions, and at many sites in the central nervous system. Its physiological and pharmacological effects, metabolism, release, and receptors have been well documented in several species. ACh has been considered an important excitatory neurotransmitter in the carotid body (CB). Various nicotinic and muscarinic ACh receptors are present in both afferent nerve endings and glomus cells. Therefore, ACh can depolarize or hyperpolarize the cell membrane depending on the available receptor type in the vicinity. Binding of ACh to its receptor can create a wide variety of cellular responses including opening cation channels (nicotinic ACh receptor activation), releasing Ca2+ from intracellular storage sites (via muscarinic ACh receptors), and modulating activities of K+ and Ca2+ channels. Interactions between ACh and other neurotransmitters (dopamine, adenosine, nitric oxide) have been known, and they may induce complicated responses. Cholinergic biology in the CB differs among species and even within the same species due to different genetic composition. Development and environment influence cholinergic biology. Pharmacological data clearly indicate that both muscarinic and nicotinic acetylcholine receptors have a role in the encoding of new memories. Localized lesions and antagonist infusions demonstrate the anatomical locus of these cholinergic effects, and computational modeling links the function of cholinergic modulation to specific cellular effects within these regions. Acetylcholine has been shown to increase the strength of afferent input relative to feedback, to contribute to theta rhythm oscillations, activate intrinsic mechanisms for persistent spiking, and increase the modification of synapses. These effects might enhance different types of encoding in different cortical structures. In particular, the effects in entorhinal and perirhinal cortex and hippocampus might be important for encoding new episodic memories. The role of ACh in attention has been repeatedly demonstrated in several tasks. Acetylcholine is linked to response accuracy in voluntary and reflexive attention and also to response speed in reflexive attention. It is well known that those with Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorders tend to be inaccurate and slow to respond. Acetylcholine has been found to be a microbial product, urinary acetylcholine is produced by Lactobacillus.
|
|
Regulatory Network
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair

