| General Information of MET (ID: META00795) |
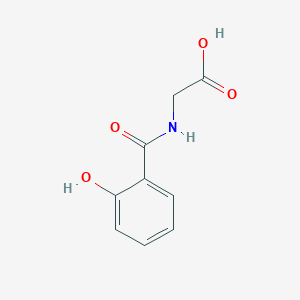
| Name |
Salicyluric acid
|
| Synonyms |
Click to Show/Hide Synonyms of This Metabolite
((2-Hydroxybenzoyl)amino)acetic acid; (2-Hydroxybenzoyl)glycine; 2-Hydroxybenzoylaminoacetate; 2-Hydroxybenzoylaminoacetic acid; 2-Hydroxybenzoylglycine; 2-Hydroxyhippurate; 2-Hydroxyhippuric acid; N-(2-Hydroxybenzoyl)-glycine; N-(2-Hydroxybenzoyl)glycine; N-(O-Hydroxybenzoyl)glycine; N-O-Hydroxybenzoylglycine; N-Salicyloylglycine; O-Hydroxy-hippurate; O-Hydroxy-hippuric acid; O-Hydroxyhippate; O-Hydroxyhippic acid; O-Hydroxyhippurate; O-Hydroxyhippuric acid; Ortho-hydroxyhippurate; Ortho-hydroxyhippuric acid; Salicylate; Salicylglycine; Salicylic acid; Salicyloylglycine; Salicylurate; Salicylurate, monosodium salt; Salicyluric acid; [(2-Hydroxybenzoyl)amino]acetate; [(2-Hydroxybenzoyl)amino]acetic acid
|
| Source |
Endogenous;Yeast Metabolite;Food;Microbial
|
| Structure Type |
Benzoic acids and derivatives (Click to Show/Hide the Complete Structure Type Hierarchy)
Benzenoids
Benzene and substituted derivatives
Benzoic acids and derivatives
|
| PubChem CID |
|
| HMDB ID |
|
| Formula |
C9H9NO4
|
| Structure |
<iframe style="width: 300px; height: 300px;" frameborder="0" src="https://embed.molview.org/v1/?mode=balls&cid=10253"></iframe>
|
 |
|
3D MOL
|
2D MOL
|
|
Click to Show/Hide the Molecular/Functional Data (External Links/Property/Function) of This Metabolite
|
| KEGG ID |
|
| ChEBI ID |
|
| FooDB ID |
|
| ChemSpider ID |
|
| METLIN ID |
|
| Physicochemical Properties |
Molecular Weight |
195.17 |
Topological Polar Surface Area |
86.6 |
| XlogP |
0.9 |
Complexity |
229 |
| Heavy Atom Count |
14 |
Rotatable Bond Count |
3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
3 |
Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
4 |
| Function |
Salicyluric acid is an aryl glycine conjugate formed by the body to eliminate excess salicylates, including aspirin. Aspirin is rapidly hydrolysed to salicylic acid which is further metabolized to various compounds, including salicyluric acid (SU) as well as various acyl and phenolic glucuronides, and hydroxylated metabolites. SU is the major metabolite of SA excreted in urine and it is present in the urine of people who have not taken salicylate drugs, although it has no anti-inflammatory effects in humans or in animals. More salicyluric acid (SU) is excreted in the urine of vegetarians than in non-vegetarians, primarily because fruits and vegetables are important sources of dietary salicylates. However, significantly less (10-15X) SU is excreted by vegetarians than individuals taking low-dose aspirin. The induction of the salicyluric acid formation is one of the saturable pathways of salicylate elimination. The formation of the methyl ester of salicyluric acid is observed during the quantitation of salicyluric acid and other salicylate metabolites in urine by high-pressure liquid chromatography. This methyl ester formation causes artificially low values for salicyluric acid and high values for salicylic acid. Salicyluric acid has been found to be a microbial metabolite.
|
|
Regulatory Network
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair

