| General Information of MET (ID: META00786) |
| Name |
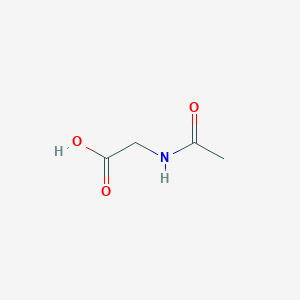
N-acetylglycine
|
| Synonyms |
Click to Show/Hide Synonyms of This Metabolite
15N-Acetylglycine a-radical; 2-Acetamidoacetate; 2-Acetamidoacetic acid; Ac gly; Ac-gly-OH; Acetamidoacetate; Acetamidoacetic acid; Acetate; Acetic acid; Aceturate; Aceturic acid; Acetylamino-acetate; Acetylamino-acetic acid; Acetylaminoacetate; Acetylaminoacetic acid; Acetylglycinate; Acetylglycine; Acetylglycocoll; Ethanoylaminoethanoate; Ethanoylaminoethanoic acid; N-Acetyl-glycine; N-Acetylglycine; N-Acetylglycine sodium salt
|
| Source |
Endogenous;Food;Drug
|
| Structure Type |
Amino acids, peptides, and analogues (Click to Show/Hide the Complete Structure Type Hierarchy)
Organic acids and derivatives
Carboxylic acids and derivatives
Amino acids, peptides, and analogues
|
| PubChem CID |
|
| HMDB ID |
|
| Formula |
C4H7NO3
|
| Structure |
<iframe style="width: 300px; height: 300px;" frameborder="0" src="https://embed.molview.org/v1/?mode=balls&cid=10972"></iframe>
|
 |
|
3D MOL
|
2D MOL
|
|
Click to Show/Hide the Molecular/Functional Data (External Links/Property/Function) of This Metabolite
|
| DrugBank ID |
|
| ChEBI ID |
|
| FooDB ID |
|
| ChemSpider ID |
|
| METLIN ID |
|
| Physicochemical Properties |
Molecular Weight |
117.1 |
Topological Polar Surface Area |
66.4 |
| XlogP |
-1.2 |
Complexity |
110 |
| Heavy Atom Count |
8 |
Rotatable Bond Count |
2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
2 |
Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
3 |
| Function |
N-acetylglycine is used is in biological research of peptidomimetics. It is used as the blocking agent of the N-terminus to prepare unnatural and unusual amino acids and amino acid analogs as well as to modify peptides. N-Substituted glycine analogs are widely used in peptidomimetics and drug research. Excessive amounts N-acetyl amino acids including N-acetylglycine (as well as N-acetylserine, N-acetylglutamine, N-acetylglutamate, N-acetylalanine, Nacetylmethionine and smaller amounts of N-acetylthreonine, N-acetylleucine, N-acetylvaline and N-acetylisoleucine) can be detected in the urine with individuals with acylase I defiency, a genetic disorder. This enzyme is involved in the degradation of N-acylated proteins. Individuals with this disorder will experience convulsions, hearing loss ond difficulty feeding.
|
|
Regulatory Network
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair

