| General Information of MET (ID: META00772) |
| Name |
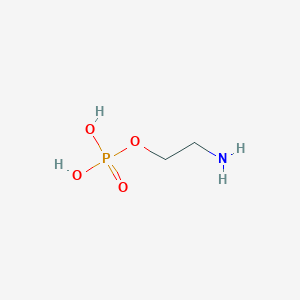
O-Phosphoethanolamine
|
| Synonyms |
Click to Show/Hide Synonyms of This Metabolite
2-Amino-ethanol dihydrogen phosphate; 2-Amino-ethanol dihydrogen phosphate (ester); 2-Amino-ethanol dihydrogen phosphoric acid; 2-Amino-ethanol phosphate; 2-Amino-ethanol phosphoric acid; 2-Aminoethanol O-phosphate; 2-Aminoethyl dihydrogen phosphate; 2-Aminoethyl dihydrogen phosphate (acd/name 4.0); 2-Aminoethyl phosphate; Calcium 2-aminoethanol phosphate; Colamine acid phosphate; Colamine phosphate; Colamine phosphoric acid; Colaminephosphoric acid; Colaminphosphate; Colaminphosphoric acid; EAP; Ethamp; Ethanolamine O-phosphate; Ethanolamine O-phosphoric acid; Ethanolamine acid phosphate; Ethanolamine acid phosphoric acid; Ethanolamine phosphate; Ethanolamine phosphoric acid; Monoaminoethyl phosphate; Monoaminoethyl phosphoric acid; O-Phosphocolamine; O-Phosphonatoethanaminium; O-Phosphorylethanolamine; OPE; PE; PEA; PETN; Phosphate 2-aminoethyl phenyl ester; Phosphoethanolamine; Phosphonoethanolamine; Phosphoric acid 2-aminoethyl phenyl ester; Phosphoryethanolamine; Phosphoryl-ethanolamine; Phosphorylethanolamine; Phosphorylethanolamine ca (1:1) salt; Phosphorylethanolamine magnesium (1:1) salt; Phosphorylethanolamine zinc salt; Phosphorylethanolamine, 3H-labeled CPD; Phosphorylethanolamine, cobalt (2+) (1:1) salt; mono(2-Aminoethyl) phosphate; mono(2-Aminoethyl) phosphoric acid
|
| Source |
Endogenous;Escherichia Coli Metabolite;Yeast Metabolite;Food;TCM Ingredients;Microbial
|
| Structure Type |
Phosphate esters (Click to Show/Hide the Complete Structure Type Hierarchy)
Organic acids and derivatives
Organic phosphoric acids and derivatives
Phosphate esters
|
| PubChem CID |
|
| HMDB ID |
|
| Formula |
C2H8NO4P
|
| Structure |
<iframe style="width: 300px; height: 300px;" frameborder="0" src="https://embed.molview.org/v1/?mode=balls&cid=1015"></iframe>
|
 |
|
3D MOL
|
2D MOL
|
|
Click to Show/Hide the Molecular/Functional Data (External Links/Property/Function) of This Metabolite
|
| KEGG ID |
|
| DrugBank ID |
|
| ChEBI ID |
|
| FooDB ID |
|
| ChemSpider ID |
|
| METLIN ID |
|
| Physicochemical Properties |
Molecular Weight |
141.06 |
Topological Polar Surface Area |
92.8 |
| XlogP |
-4.8 |
Complexity |
98.2 |
| Heavy Atom Count |
8 |
Rotatable Bond Count |
3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
3 |
Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
5 |
| Function |
Phosphoethanolamine (PE) is a phosphomonoester metabolite of the phospholipid metabolism. PE is a precursor of phospholipid synthesis and a product of phospholipid breakdown. Phosphomonoesters are present at much higher levels in brain than in other organs. In developing brain, phosphomonoesters are normally elevated during the period of neuritic proliferation. This also coincides with the occurrence of normal programmed cell death and synaptic pruning in developing brain. These findings are consistent with the role of phosphomonoesters in membrane biosynthesis. PE shows a strong structural similarity to the inhibitory neurotransmitter, GABA, and the GABAB receptor partial agonist, 3-amino-propylphosphonic acid. PE is a phosphomonoester which is decreased in post-mortem Alzheimer's disease (AD) brain.
|
|
Regulatory Network
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair

