|
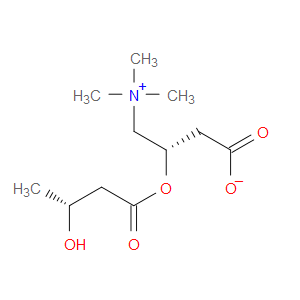
3-Hydroxybutyrylcarnitine, also known as hydroxybutyrylcarnitine, is classified as a member of the acyl carnitines. Acyl carnitines are organic compounds containing a fatty acid with the carboxylic acid attached to carnitine through an ester bond. 3-Hydroxybutyrylcarnitine is considered to be a slightly soluble (in water) and a weak acidic compound. 3-Hydroxybutyrylcarnitine is a fatty ester lipid molecule. 3-Hydroxybutyrylcarnitine can be found in blood. Within a cell, 3-hydroxybutyrylcarnitine is primarily located in the extracellular space and near the membrane.
|
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair