|
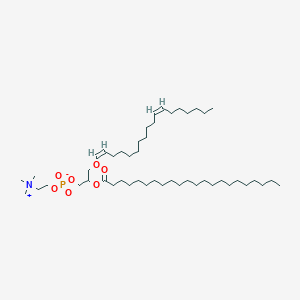
PC(P-18:1(11Z)/22:0) is a phosphatidylcholine (PC or GPCho). It is a glycerophospholipid in which a phosphorylcholine moiety occupies a glycerol substitution site. As is the case with diacylglycerols, glycerophosphocholines can have many different combinations of fatty acids of varying lengths and saturation attached at the C-1 and C-2 positions. Fatty acids containing 16, 18 and 20 carbons are the most common. PC(P-18:1(11Z)/22:0), in particular, consists of one chain of plasmalogen 18:1n7 at the C-1 position and one chain of behenic acid at the C-2 position. The plasmalogen 18:1n7 moiety is derived from animal fats, liver and kidney, while the behenic acid moiety is derived from groundnut oil. Phospholipids, are ubiquitous in nature and are key components of the lipid bilayer of cells, as well as being involved in metabolism and signaling. While most phospholipids have a saturated fatty acid on C-1 and an unsaturated fatty acid on C-2 of the glycerol backbone, the fatty acid distribution at the C-1 and C-2 positions of glycerol within phospholipids is continually in flux, owing to phospholipid degradation and the continuous phospholipid remodeling that occurs while these molecules are in membranes. PCs can be synthesized via three different routes. In one route, choline is activated first by phosphorylation and then by coupling to CDP prior to attachment to phosphatidic acid. PCs can also synthesized by the addition of choline to CDP-activated 1,2-diacylglycerol. A third route to PC synthesis involves the conversion of either PS or PE to PC. Plasmalogens are glycerol ether phospholipids. They are of two types, alkyl ether (-O-CH2-) and alkenyl ether (-O-CH=CH-). Dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) serves as the glycerol precursor for the synthesis of plasmalogens. Three major classes of plasmalogens have been identified: choline, ethanolamine and serine derivatives. Ethanolamine plasmalogen is prevalent in myelin. Choline plasmalogen is abundant in cardiac tissue. Usually, the highest proportion of the plasmalogen form is in the ethanolamine class with rather less in choline, and commonly little or none in other phospholipids such as phosphatidylinositol. In choline plasmalogens of most tissues, a higher proportion is often of the O-alkyl rather than the O-alkenyl form, but the reverse tends to be true in heart lipids. In animal tissues, the alkyl and alkenyl moieties in both non-polar and phospholipids tend to be rather simple in composition with 16:0, 18:0 and 18:1 (double bond in position 9) predominating. Ether analogues of triacylglycerols, i.e. 1-alkyldiacyl-sn-glycerols, are present at trace levels only if at all in most animal tissues, but they can be major components of some marine lipids.
|
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair