| General Information of MET (ID: META00588) |
| Name |
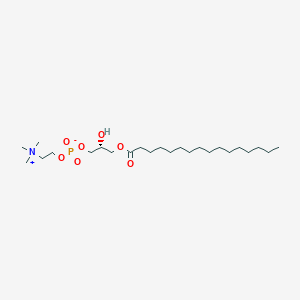
LysoPC(16:0/0:0)
|
| Synonyms |
Click to Show/Hide Synonyms of This Metabolite
(2R)-2-Hydroxy-3-(hexadecanoyloxy)propyl 2-(trimethylazaniumyl)ethyl phosphate; (2R)-2-Hydroxy-3-(hexadecanoyloxy)propyl 2-(trimethylazaniumyl)ethyl phosphoric acid; 1-16:0-LysoPC; 1-16:0-Lysophosphatidylcholine; 1-Hexadecanoyl-2-lysophosphatidylcholine; 1-Hexadecanoyl-3-glycerophosphorylcholine; 1-Hexadecanoyl-glycero-3-phosphocholine; 1-Hexadecanoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine; 1-Hexadecanoyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphorylcholine; 1-Hexadecanoylglycerophosphocholine; 1-Hexadecanoyllysolecithin; 1-Hexadecyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine; 1-O-Hexadecylpropanediol 3-phosphorylcholine; 1-O-Palmitoyl-2-lyso-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine; 1-O-Palmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine; 1-O-Palmitoyl-sn-glyceryl-3-phosphorylcholine; 1-Palmitoyl-2-hydroxy-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine; 1-Palmitoyl-2-lyso-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine; 1-Palmitoyl-2-lysophosphatidylcholine; 1-Palmitoyl-3-glycerylphosphorylcholine; 1-Palmitoyl-GPC; 1-Palmitoyl-GPC (16:0); 1-Palmitoyl-glycero-3-phosphocholine; 1-Palmitoyl-lysophosphatidylcholine; 1-Palmitoyl-phosphatidylcholine; 1-Palmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine; 1-Palmitoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphorylcholine; 1-Palmitoyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphatidylcholine; 1-Palmitoyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphocholine; 1-Palmitoyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphorylcholine; 1-Palmitoylglycerol-3-phosphorylcholine; 1-Palmitoylglycerophosphocholine; 1-Palmitoyllecithin; 1-Palmitoyllysolecithin; 1-Palmitoyllysophosphatidylcholine; 1-Palmitoylphosphatidylcholine; 1-Pam-2-lysoptdcho; 16:0 LYSO-PC; C(16)-Lysophosphatidylcholine; GPC(16:0); GPC(16:0/0:0); GPCho 16:0/0:0; GPCho(16:0/0:0); Hydroxide inner salt(+-)-isomer OF we 201; Hydroxide inner salt(R)-isomer OF we 201; Hydroxide inner salt(S)-isomer OF we 201; L-Palmitoyllysolecithin; L-alpha-Lysopalmitoylphosphatidylcholine; LPC 16:0/0:0; LPC(16:0); LPC(16:0/0:0); LYSO-PC; LyPC(16:0); LyPC(16:0/0:0); LysoPC 16:0/0:0; LysoPC a C16:0; LysoPC(16:0); LysoPC(16:0/0:0); Lysophosphatidylcholine C16:0; Lysophosphatidylcholine(16:0); Lysophosphatidylcholine(16:0/0:0); MPPC; PC(16:0/0:0); Palmitoyl L-alpha-lysolecithin; Palmitoyl L-alpha-lysophosphatidylcholine; Palmitoyl lysophosphatidylcholine; Palmitoyllysolecithin; Palmitoyllysophosphatidyl choline
|
| Source |
Aliphatic acyclic compounds
|
| Structure Type |
Glycerophosphocholines (Click to Show/Hide the Complete Structure Type Hierarchy)
Lipids and lipid-like molecules
Glycerophospholipids
Glycerophosphocholines
|
| PubChem CID |
|
| HMDB ID |
|
| Formula |
C24H50NO7P
|
| Structure |
<iframe style="width: 300px; height: 300px;" frameborder="0" src="https://embed.molview.org/v1/?mode=balls&cid=460602"></iframe>
|
 |
|
3D MOL is unavailable
|
2D MOL
|
|
Click to Show/Hide the Molecular/Functional Data (External Links/Property/Function) of This Metabolite
|
| KEGG ID |
|
| ChEBI ID |
|
| FooDB ID |
|
| ChemSpider ID |
|
| Physicochemical Properties |
Molecular Weight |
495.6 |
Topological Polar Surface Area |
105 |
| XlogP |
5.6 |
Complexity |
517 |
| Heavy Atom Count |
33 |
Rotatable Bond Count |
24 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
1 |
Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
7 |
| Function |
LysoPC(16:0) is a lysophospholipid (LyP). It is a monoglycerophospholipid in which a phosphorylcholine moiety occupies a glycerol substitution site. Lysophosphatidylcholines can have different combinations of fatty acids of varying lengths and saturation attached at the C-1 (sn-1) position. Fatty acids containing 16, 18 and 20 carbons are the most common. LysoPC(16:0), in particular, consists of one chain of palmitic acid at the C-1 position. The palmitic acid moiety is derived from fish oils, milk fats, vegetable oils and animal fats. Lysophosphatidylcholine is found in small amounts in most tissues. It is formed by hydrolysis of phosphatidylcholine by the enzyme phospholipase A2, as part of the de-acylation/re-acylation cycle that controls its overall molecular species composition. It can also be formed inadvertently during extraction of lipids from tissues if the phospholipase is activated by careless handling. In blood plasma significant amounts of lysophosphatidylcholine are formed by a specific enzyme system, lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT), which is secreted from the liver. The enzyme catalyzes the transfer of the fatty acids of position sn-2 of phosphatidylcholine to the free cholesterol in plasma, with formation of cholesterol esters and lysophosphatidylcholine. Lysophospholipids have a role in lipid signaling by acting on lysophospholipid receptors (LPL-R). LPL-R's are members of the G protein-coupled receptor family of integral membrane proteins.
|
|
Regulatory Network
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair

