| General Information of MET (ID: META00364) |
| Name |
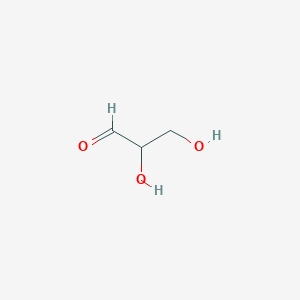
Glyceraldehyde
|
| Synonyms |
Click to Show/Hide Synonyms of This Metabolite
(+-)-Glyceraldehyde; (+/-)-2,3-dihydroxy-propanal; (+/-)-glyceraldehyde; 2,3-Dihydroxypropanal; 2,3-Dihydroxypropionaldehyde; Aldotriose; D-(+)-Glyceraldehyde; D-2,3-Dihydroxypropanal; D-2,3-Dihydroxypropionaldehyde; D-Aldotriose; D-Glyceraldehyde; D-Glycerose; DL-Glyceraldehyde; Dihydroxypropionaldehyde; Gliceraldehido; Glyceraldehyd; Glyceric aldehyde; Glycerinaldehyd; Glycerinaldehyde; Glycerinformal; Glycerose; Glyzerinaldehyd; alpha,beta-Dihydroxypropionaldehyde; delta-(+)-Glyceraldehyde; delta-2,3-Dihydroxypropanal; delta-2,3-Dihydroxypropionaldehyde; delta-Aldotriose; delta-Glyceraldehyde; delta-Glycerose
|
| Source |
Endogenous;Escherichia Coli Metabolite;Food;Toxins/Pollutant;Microbial
|
| Structure Type |
Carbohydrates and carbohydrate conjugates (Click to Show/Hide the Complete Structure Type Hierarchy)
Organic oxygen compounds
Organooxygen compounds
Carbohydrates and carbohydrate conjugates
|
| PubChem CID |
|
| HMDB ID |
|
| Formula |
C3H6O3
|
| Structure |
<iframe style="width: 300px; height: 300px;" frameborder="0" src="https://embed.molview.org/v1/?mode=balls&cid=751"></iframe>
|
 |
|
3D MOL
|
2D MOL
|
|
Click to Show/Hide the Molecular/Functional Data (External Links/Property/Function) of This Metabolite
|
| KEGG ID |
|
| ChEBI ID |
|
| FooDB ID |
|
| ChemSpider ID |
|
| METLIN ID |
|
| Physicochemical Properties |
Molecular Weight |
90.08 |
Topological Polar Surface Area |
57.5 |
| XlogP |
-1.6 |
Complexity |
43.3 |
| Heavy Atom Count |
6 |
Rotatable Bond Count |
2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
2 |
Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
3 |
| Function |
Glyceraldehyde is a triose monosaccharide with chemical formula C3H6O3. It is the simplest of all common aldoses. It is a sweet, colourless crystalline solid that is an intermediate compound in carbohydrate metabolism. The word "glyceraldehyde" comes from combining glycerine and aldehyde, as glyceraldehyde is merely glycerine with one hydroxide changed to an aldehyde. Glyceraldehyde is produced from the action of the enzyme glyceraldehyde dehydrogenase, which converts glycerol to glyceraldehyde using NADP as a cofactor. When present at sufficiently high levels, glyceraldehyde can be a cytotoxin and a mutagen. A cytotoxin is a compound that kills cells. A mutagen is a compound that causes mutations in DNA. Glyceraldehyde is a highly reactive compound that can modify and cross-link proteins. Glyceraldehyde-modified proteins appear to be cytotoxic, depress intracellular glutathione levels, and induce reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. Glyceraldehyde has been shown to cause chromosome damage to human cells in culture and is mutagenic in the Ames bacterial test.
|
|
Regulatory Network
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair

