|
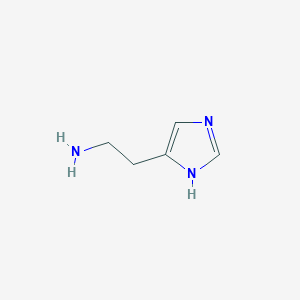
Histamine is an amine derived by enzymatic decarboxylation of histidine. It is a powerful stimulant of gastric secretion, a constrictor of bronchial smooth muscle, a vasodilator, and also a centrally acting neurotransmitter. Histamine can be found in Photobacterium phosphoreum and Lactobacillus. Histamine belongs to the class of organic compounds known as 2-arylethylamines. These are primary amines that have the general formula RCCNH2, where R is an organic group. Outside of the human body, histamine is found, on average, in the highest concentration in a few different foods, such as spinach, oats, and ryes, and in a lower concentration in green beans, broccoli, and red beetroots. Histamine has also been detected, but not quantified in, several different foods, such as groundcherries, carobs, bok choy, biscuits, and longans. This could make histamine a potential biomarker for the consumption of these foods.
|
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair