|
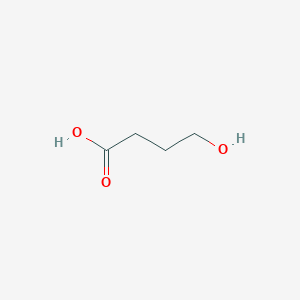
4-Hydroxybutyric acid (also known as gamma-hydroxybutyrate or GHB) is a precursor and a metabolite of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). GHB acts as a central nervous system (CNS) neuromodulator, mediating its effects through GABA and GHB-specific receptors, or by affecting dopamine transmission. GHB occurs naturally in all mammals, but its function remains unknown. GHB is labeled as an illegal drug in most countries, but it also is used as a legal drug (Xyrem) in patients with narcolepsy. It is used illegally (under the street names juice, liquid ecstasy, or G) as an intoxicant for increasing athletic performance and as a date rape drug. In high doses, GHB inhibits the CNS, inducing sleep and inhibiting the respiratory drive. In lower doses, its euphoriant effect predominates. When present in sufficiently high levels, 4-hydroxybutyric acid can act as an acidogen, a neurotoxin, and a metabotoxin. An acidogen is an acidic compound that induces acidosis, which has multiple adverse effects on many organ systems. A neurotoxin is a compound that adversely affects neural cells and tissues. A metabotoxin is an endogenously produced metabolite that causes adverse health effects at chronically high levels. Chronically high levels of 4-hydroxybutyric acid are associated with two inborn errors of metabolism: glutaric aciduria II and succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency (SSADH). SSADH deficiency leads to a 30-fold increase of GHB and a 2-4 fold increase of GABA in the brains of patients with SSADH deficiency as compared to normal brain concentrations of the compounds. As an acidogen, 4-hydroxybutyric acid is an organic acid, and abnormally high levels of organic acids in the blood (organic acidemia), urine (organic aciduria), the brain, and other tissues lead to general metabolic acidosis. Acidosis typically occurs when arterial pH falls below 7.35. In infants with acidosis, the initial symptoms include poor feeding, vomiting, loss of appetite, weak muscle tone (hypotonia), and lack of energy (lethargy). These can progress to heart abnormalities, kidney abnormalities, liver damage, seizures, coma, and possibly death. Many affected children with organic acidemias experience intellectual disability or delayed development. These are also the characteristic symptoms of the untreated IEMs mentioned above. Particularly for SSADH deficiency, the most common features observed include developmental delay, hypotonia, and intellectual disability. Nearly half of patients exhibit ataxia, seizures, behaviour problems, and hyporeflexia. In adults, acidosis or acidemia is characterized by headaches, confusion, feeling tired, tremors, sleepiness, and seizures. As a neurotoxin, GHB appears to affect both GABA (a neurotransmitter) signaling and glutamate signaling (another neurotransmitter). Glutamine metabolism may also play a role in the pathophysiology of excessive levels of GHB. High levels of GHB have been shown to depress both the NMDA and AMPA/kainite receptor-mediated functions and may also alter glutamatergic excitatory synaptic transmission as well. 4-Hydroxybutyric acid is a microbial metabolite found in Aeromonas, Escherichia and Pseudomonas.
|
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair