| General Information of MET (ID: META00290) |
| Name |
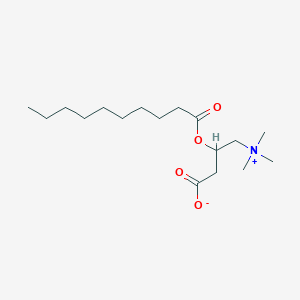
Decanoylcarnitine
|
| Synonyms |
Click to Show/Hide Synonyms of This Metabolite
Decanoyl-L-carnitine; Decanoylcarnitine, (+-)-isomer; Decanoylcarnitine, (R)-isomer; Decanoylcarnitine, (S)-isomer
|
| Source |
Endogenous;Fatty acyls;Food
|
| Structure Type |
Fatty acid esters (Click to Show/Hide the Complete Structure Type Hierarchy)
Lipids and lipid-like molecules
Fatty Acyls
Fatty acid esters
|
| PubChem CID |
|
| HMDB ID |
|
| Formula |
C17H33NO4
|
| Structure |
<iframe style="width: 300px; height: 300px;" frameborder="0" src="https://embed.molview.org/v1/?mode=balls&cid=10245190"></iframe>
|
 |
|
3D MOL
|
2D MOL
|
|
Click to Show/Hide the Molecular/Functional Data (External Links/Property/Function) of This Metabolite
|
| ChEBI ID |
|
| FooDB ID |
|
| ChemSpider ID |
|
| METLIN ID |
|
| Physicochemical Properties |
Molecular Weight |
315.4 |
Topological Polar Surface Area |
66.4 |
| XlogP |
4.5 |
Complexity |
318 |
| Heavy Atom Count |
22 |
Rotatable Bond Count |
13 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
N.A. |
Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
4 |
| Function |
Decanoylcarnitine is a member of the class of compounds known as acylcarnitines. Acylcarnitines are organic compounds containing a fatty acid with the carboxylic acid attached to carnitine through an ester bond. Thus, decanoylcarnitine is considered to be a fatty ester lipid molecule. Decanoylcarnitine is practically insoluble (in water) and a weakly acidic compound (based on its pKa). Decanoylcarnitine can be found in blood, feces, and urine. Within the cell, decanoylcarnitine is primarily located in the membrane. It can also be found in the extracellular space. Acylcarnitines are useful in the diagnosis of genetic disorders such as fatty acid oxidation disorders and differentiation between biochemical phenotypes of medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (MCAD) deficiency disorders. Moreover, decanoylcarnitine is found to be associated with very long chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (VLAD) deficiency, glutaric aciduria II, and celiac disease, which are inborn errors of metabolism.
|
|
Regulatory Network
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair

