|
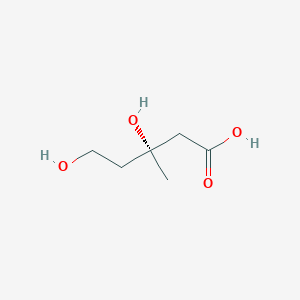
Mevalonic acid (CAS: 150-97-0), also known as MVA, mevalonate, or hiochic acid, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as hydroxy fatty acids. These are fatty acids in which the chain bears a hydroxyl group. Mevalonic acid is a very hydrophobic molecule, practically insoluble (in water), and relatively neutral. Mevalonic acid is found, on average, in the highest concentration within a few different foods, such as apples, corns, and wild carrots and in a lower concentration in garden tomato (var.), pepper (C. frutescens), and cucumbers. Mevalonic acid has also been detected, but not quantified in, several different foods, such as sweet oranges, potato, milk (cow), cabbages, and white cabbages. This could make mevalonic acid a potential biomarker for the consumption of these foods. Mevalonic acid is a key organic compound in biochemistry. The production of mevalonic acid by the enzyme 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase, is the rate-limiting step in the biosynthesis of cholesterol. Plasma concentrations and urinary excretion of MVA are decreased by HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor drugs such as pravastatin, simvastatin, and atorvastatin.
|
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair