| General Information of MET (ID: META00123) |
| Name |
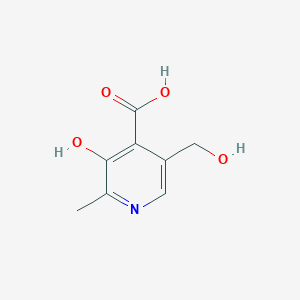
4-Pyridoxic acid
|
| Synonyms |
Click to Show/Hide Synonyms of This Metabolite
2-Methyl-3-hydroxy-4-carboxy-5-hydroxymethylpyridine; 3-Hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methyl-4-pyridinecarboxylate; 3-Hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methyl-4-pyridinecarboxylic acid; 3-Hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methyl-isonicotinate; 3-Hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methyl-isonicotinic acid; 3-Hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methylisonicotinate; 3-Hydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-2-methylisonicotinic acid; 3-Hydroxy-5-hydroxymethyl-2-methyl-isonicotinate; 3-Hydroxy-5-hydroxymethyl-2-methyl-isonicotinic acid; 3-Hydroxy-5-hydroxymethyl-2-methyl-isonicotinsaeure; 4 Pyridoxic acid; 4 Pyridoxinic acid; 4 Pyridoxylic acid; 4-Pyridoxate; 4-Pyridoxinate; 4-Pyridoxinecarboxylate; 4-Pyridoxinecarboxylic acid; 4-Pyridoxinic acid; 4-Pyridoxinsaeure; 4-Pyridoxylate; 4-Pyridoxylic acid; Pyridoxate; Pyridoxic acid; Pyridoxinecarboxylic acid
|
| Source |
Endogenous;Escherichia Coli Metabolite;Food;Microbial
|
| Structure Type |
Pyridinecarboxylic acids and derivatives (Click to Show/Hide the Complete Structure Type Hierarchy)
Organoheterocyclic compounds
Pyridines and derivatives
Pyridinecarboxylic acids and derivatives
|
| PubChem CID |
|
| HMDB ID |
|
| Formula |
C8H9NO4
|
| Structure |
<iframe style="width: 300px; height: 300px;" frameborder="0" src="https://embed.molview.org/v1/?mode=balls&cid=6723"></iframe>
|
 |
|
3D MOL
|
2D MOL
|
|
Click to Show/Hide the Molecular/Functional Data (External Links/Property/Function) of This Metabolite
|
| KEGG ID |
|
| ChEBI ID |
|
| FooDB ID |
|
| ChemSpider ID |
|
| METLIN ID |
|
| Physicochemical Properties |
Molecular Weight |
183.16 |
Topological Polar Surface Area |
90.6 |
| XlogP |
0.1 |
Complexity |
197 |
| Heavy Atom Count |
13 |
Rotatable Bond Count |
2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count |
3 |
Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count |
5 |
| Function |
4-Pyridoxic acid is the catabolic product of vitamin B6 (also known as pyridoxine, pyridoxal and pyradoxamine) which is excreted in the urine. Urinary levels of 4-pyridoxic acid are lower in females than in males and will be reduced in persons with riboflavin deficiency. 4-Pyridoxic acid is formed by the action of aldehyde oxidase I (an endogenous enzyme) and by microbial enzymes (pyridoxal 4-dehydrogenase), an NAD-dependent aldehyde dehydrogenase. 4-pyridoxic acid can be further broken down by the gut microflora via 4-pyridoxic acid dehydrogenase. This enzyme catalyzes the four electron oxidation of 4-pyridoxic acid to 3-hydroxy-2-methylpyridine-4,5-dicarboxylate, using nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide as a cofactor.
|
|
Regulatory Network
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 click to show the details of this protein
click to show the details of this protein
 click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair
click to show the details of experiment for validating this pair

